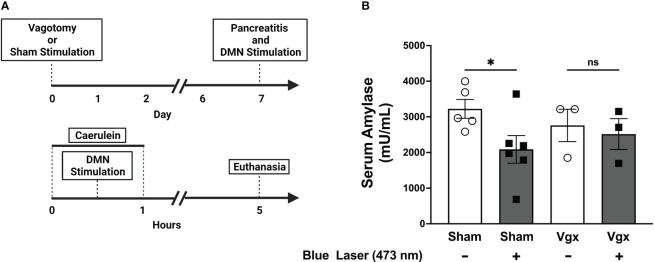
Figure 4.
Selective activation of DMN cholinergic neurons fails to reduce serum amylase levels in mice subjected to subdiaphragmatic vagotomy. (A) A bilateral subdiaphragmatic vagotomy and transgastric pyloric dilation or sham surgery, consisting of celiotomy and transgastric pyloric dilation only, were performed on ChAT-ChR2-YFP mice. After one week of recovery, pancreatitis was induced with two intraperitoneal injections of caerulein (50 µg/kg). The mice were subjected to optogenetic stimulation with blue light or sham stimulation. The mice were euthanized 4 hours after the final dose of caerulein. (B) Optogenetic stimulation with blue light significantly decreases serum amylase levels in sham-operated mice (Sham), but not in mice subjected to subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (Vgx). Data are represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Kruskal-Wallis test, (*P ≤ 0.05, n = 3-6), ns, not significant.