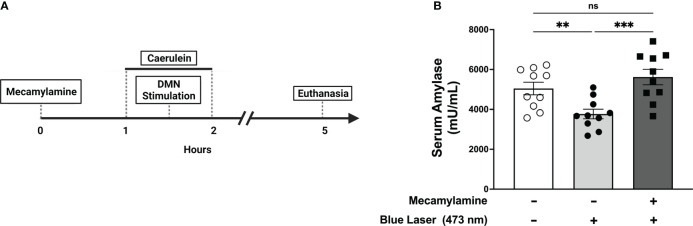
Figure 5.
Selective activation of DMN cholinergic neurons reduces serum amylase levels during pancreatitis through a nAChR-dependent mechanism. (A) One hour prior to induction of acute pancreatitis, ChAT-ChR2-YFP mice underwent intraperitoneal injection of vehicle or mecamylamine (1 mg/kg) was injected one hour prior followed by the induction of pancreatitis and optogenetic stimulation. The mice were euthanized 4 hours after the final dose of caerulein. (B) Optogenetic stimulation with blue light (473 nm, 20 Hz, 25% duty cycle, 8-12 mW, 5 minutes) of the DMN significantly decreases the level of serum amylase compared to no stimulation in the vehicle-treated mice but not in animals receiving mecamylamine. Data are represented as individual mouse data points with mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA, (**P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, n = 10, ns, not significant.).