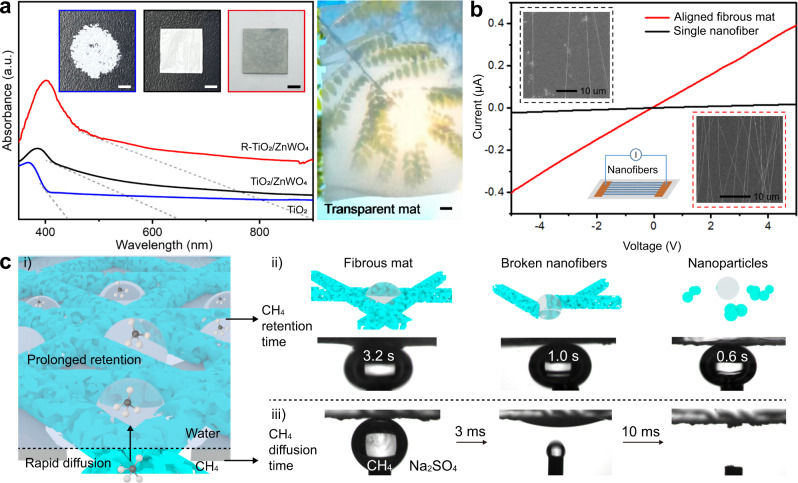
Fig. 4. Optical, electrical and triphasic interfacial properties of fibrous mat.
a UV–vis absorption spectra of R-TiO2/ZnWO4, TiO2/ZnWO4 and TiO2. Insets in spectra show the optical images of non-free-standing TiO2, free-standing TiO2/ZnWO4 and R-TiO2/ZnWO4 mat. The optical image (right) shows a transparent TiO2/ZnWO4 fibrous mat. The scale bars represent 5 mm in (a). b The inherent conductivity test of R-TiO2/ZnWO4 with and without fibrous interwoven structure. The inset SEM images and schemes illustrate the fibrous structures and the test method, respectively. c Schematic illustration of the triphasic interfaces in the designed R-TiO2/ZnWO4/PTFE mat (i). The contact angles of CH4 gas bubbles on the surfaces of R-TiO2/ZnWO4 fibrous mat (ii, left), on broken nanofibers (ii, middle), and on nanoparticles (ii, right) in the same Na2SO4 (pH = 2) liquid. The inserted schemes illustrate these structures. The contact angle of CH4 gas bubbles on the surface of PTFE shows the rapid gas diffusion into R-TiO2/ZnWO4 (iii).