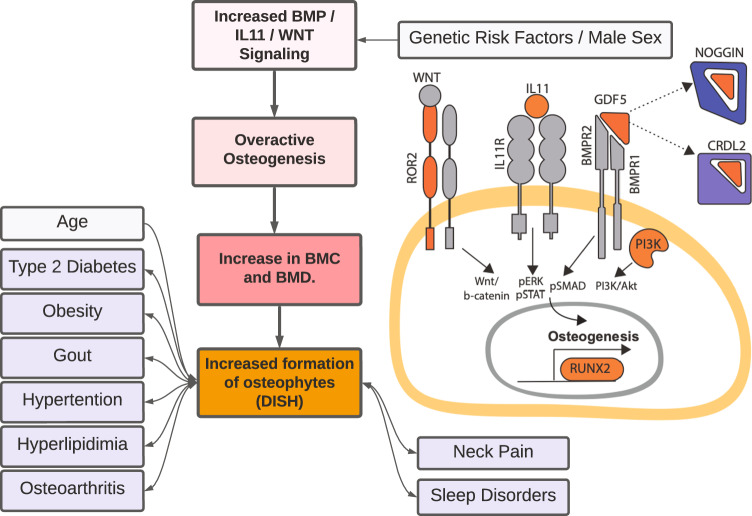
Fig. 6. Overview of genetic and environmental risk factors associated with development of DISH.
In addition to male sex and age, pre-existing conditions such T2D, obesity, and osteoarthritis are risk factors associated with DISH. Genetic analysis (GWAS, colocalization, and Mendelian randomization) points to genes involved in overactive osteogenesis as drivers of the pathology (highlighted in orange). The increase in osteogenesis, and consequence in increases in BMD and BMC measures is observed throughout the entire body. Molecular mechanisms likely involve gain of function in multiple signaling pathways such Wnt signaling, IL11 signaling, and BMP-signaling. Conversely, loss of inhibitory BMP proteins such as Noggin and CRDL2 likely increases BMP-signaling. In prognostic outcomes, DISH is associated with increased risk of metabolic and sleep disorder diagnoses.