Fig. 1.
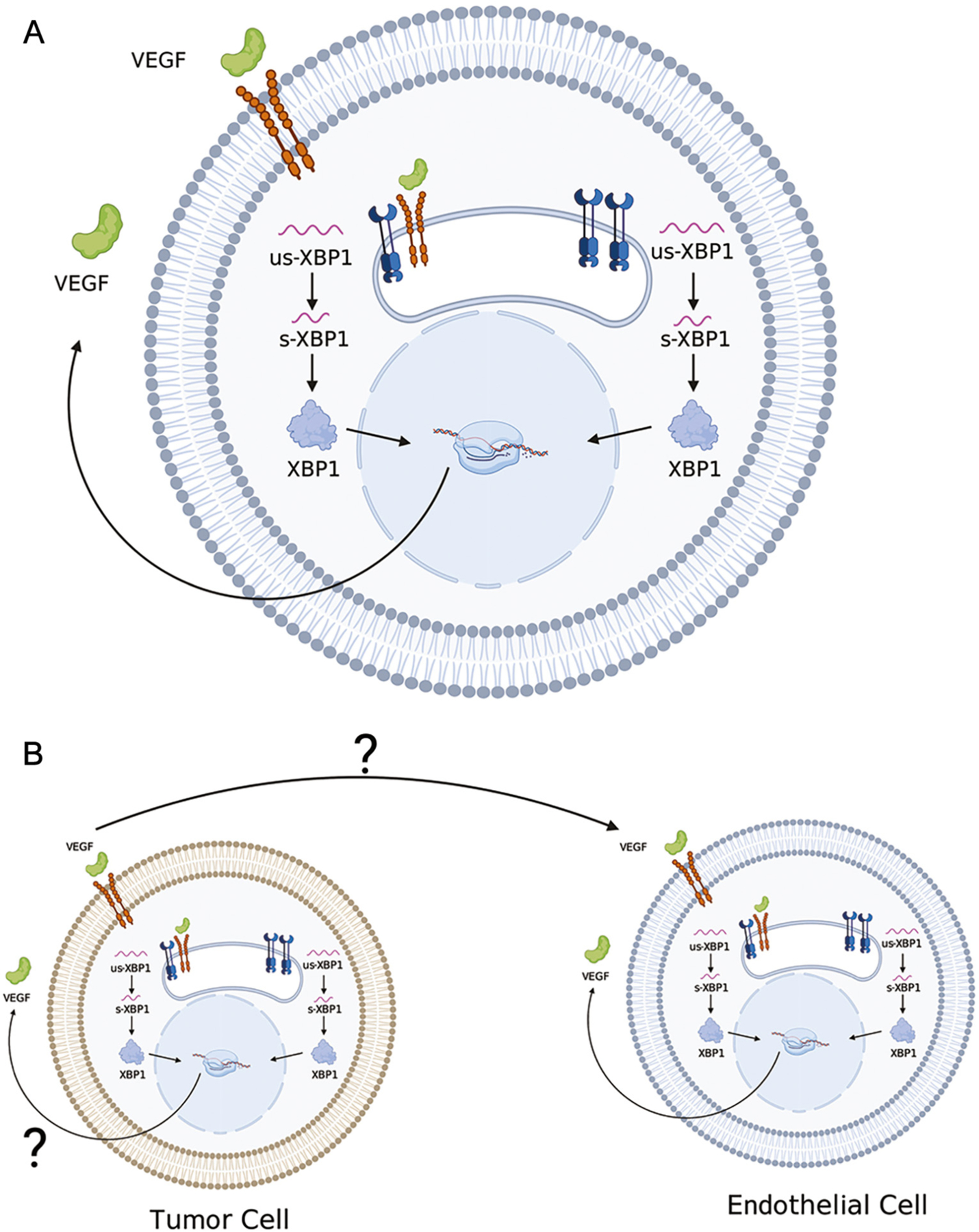
VEGF-IRE1α interactions in UPR. (A) In endothelial cells, binding of VEGF to the VEGF2R causes internalization of VEGFR2 [1]. Internalized VEGFR2 then heterodimerizes with IRE1α at the ER membrane and activates the XBP-1 splicing complex [1]. XBP1 also activates the Akt/GSK/bcatenin axis to drive cell proliferation and growth, and increased VEGF transcription, translation and secretion [1]. VEGF via membrane VEGFR2 activates signaling pathways that rapidly enhance angiogenesis. (B) Both tumor cell-derived VEGF and endothelial cell-derived VEGF may act via paracrine and autocrine mechanisms to promote vascularization (65, 66).
