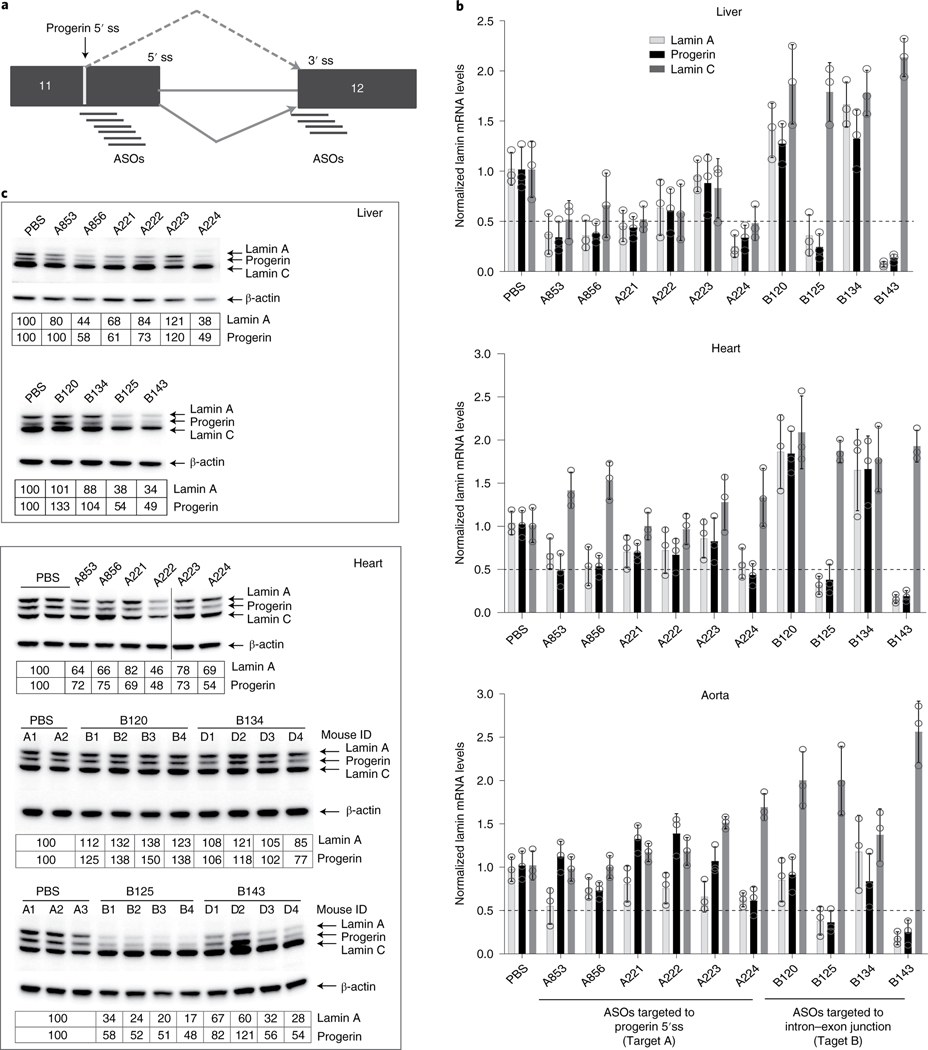
Fig. 3 |. in vivo screen to identify efficient LMNA ASO.
The top ten ASOs from in vitro screen were re-tested in G608G transgenic mice. a, Schematic diagram of alternative progerin 5′ splice site and intron 11–exon 12 splice junction target sites. b, Quantification of lamin A, progerin and lamin C mRNA by ddPCR. LMNAG/+ mice (n = 4 per group) were treated with PBS or LMNA ASOs (50 mg kg−1) as described for 4 weeks (Methods). Total RNA from liver, heart and aorta was isolated, and lamin A, progerin and lamin C mRNAs were measured by ddPCR using human-specific primers and probe (Methods). Data are from at least three mice per group averaged from two separate assays, are normalized to housekeeping gene mTfrc and are presented as mean ± s.d. c, Western blot analysis. Total protein extract from heart and liver was prepared, and the expression of lamin A, progerin and lamin C was measured using anti-lamin A/C antibody (sc376248) (Methods). The data are representative of two experiments, are normalized to housekeeping β-actin and are expressed relative to control (PBS) treatment. ss, splice site.