Fig. 2.
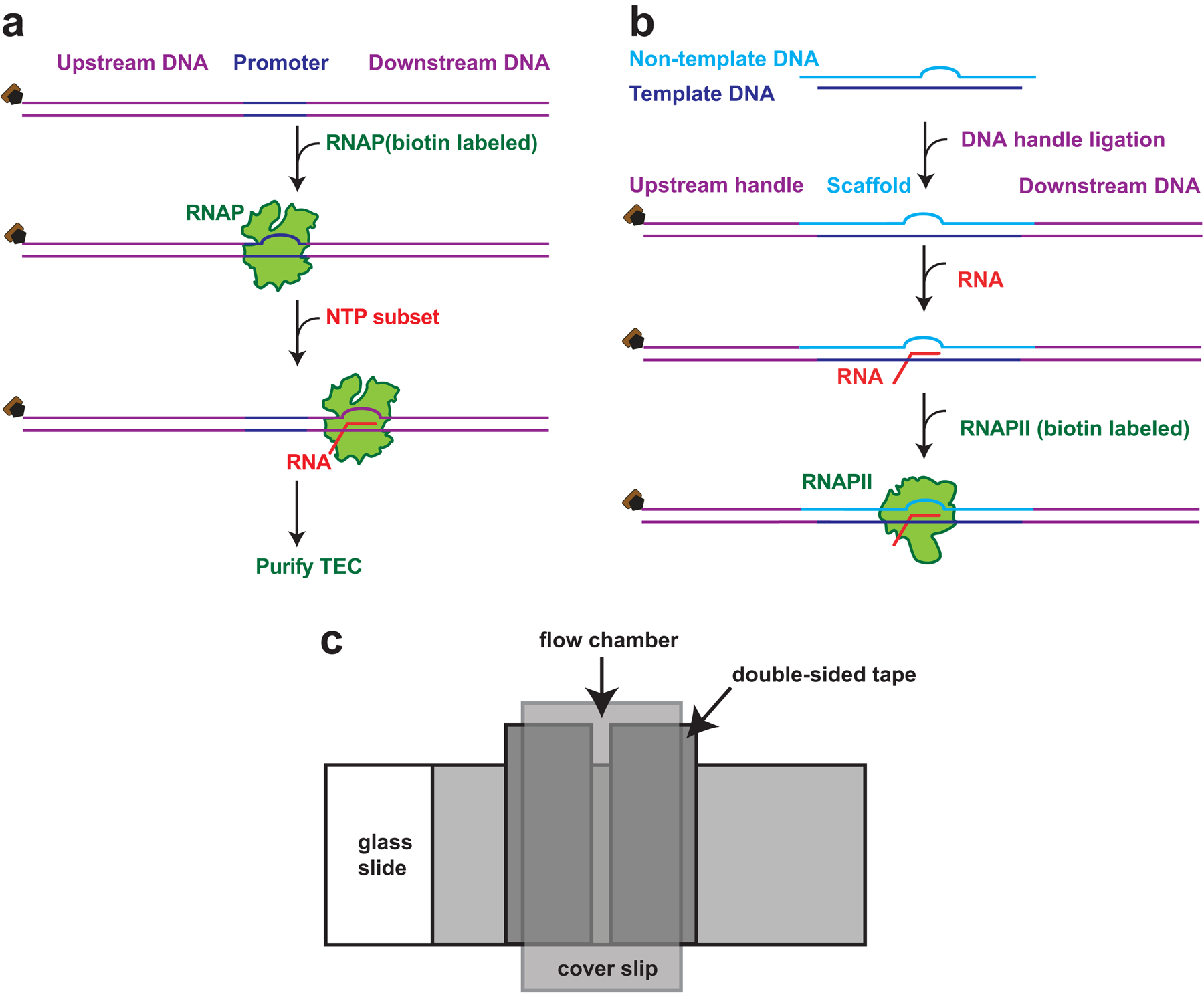
(a). Schematic representation of steps to assemble E. coli TEC. A DNA template (purple) containing a promoter sequence (yellow) is incubated with a RNAP and a subset of NTPs. RNAP is stalled at the nucleotide deficient site and forms a TEC, which can then be purified and used for optical trapping. (b). Schematic representation of steps for reconstituting RNAPII TEC. Non-template DNA (light blue) containing an 11 nt of non-complementary sequence anneals to a template DNA (dark blue) and forms a scaffold containing an artificial transcription bubble. The scaffold is ligated to an upstream DNA handle and a downstream DNA template (both in purple), and annealed to a 14 nt RNA fragment (red). Biotin labeled RNAPII (green) is incubated with the scaffold to forms the TEC. (c). Schematic diagram of a typical flow cell assembly. Two strips of double-sided tape, separated by 1.5–2 mm, are applied to a glass slide. A plasma-cleaned cover glass is then applied to the double-sided tape, allowing a flow chamber to be formed between glass slide and cover glass. The assembly is then pressed to seal the flow chamber.
