Figure 1.
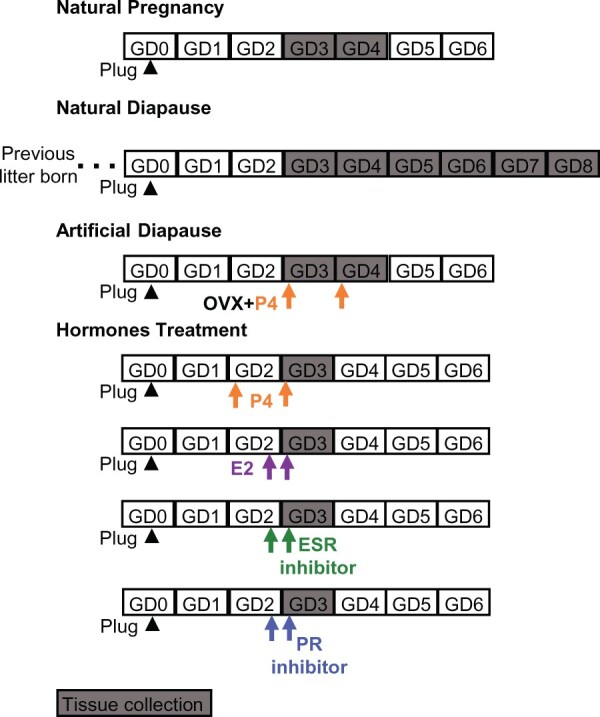
Schematic of mouse models used to study the effects of ovarian hormone modulation on embryo location. Natural pregnancy analysis is performed in the first pregnancy of a virgin post-pubertal mouse. For natural (lactational) diapause, the female mouse gives birth to its first litter and mates with a male within 48 h owing to post-partum estrous, and the resulting pregnancy is analyzed. Artificial diapause is a delay in implantation induced under laboratory conditions by removing the ovaries during the first pregnancy of a virgin mouse, and only progesterone (P4) is injected to keep the pregnancy active. To corroborate results obtained from these models, we also use exogenous hormone (estrogen (E2) or P4) administration or estrogen receptor (ESR) and P4 receptor (PR) inhibitor on gestational day (GD) 2 or/and GD3 to understand their effect on embryo movement. Arrowhead is GD0 1200 h when plug is identified. Arrow indicates the injection time. OVX: ovariectomy.
