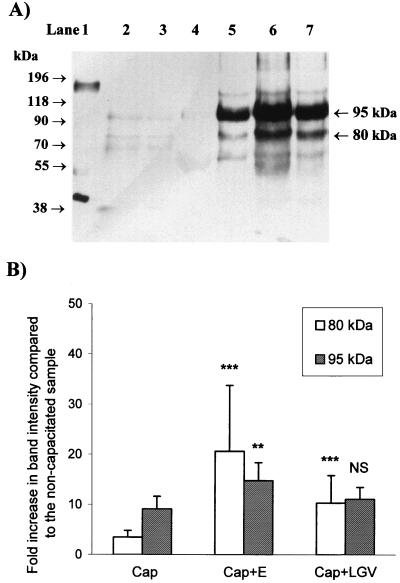
FIG. 2.
Effect of C. trachomatis serovars E and LGV on protein tyrosine phosphorylation in human spermatozoa. (A) Typical Western blotting result. Human spermatozoa (106 per lane) were incubated under noncapacitating (lane 4) or capacitating (lanes 5 through 7) conditions in the absence of C. trachomatis (lane 5) or with serovar E (lane 6) or with serovar LGV (lane 7) C. trachomatis. Samples containing only serovar E or LGV (lanes 2 and 3, respectively; 10 to 15 times more than incubated with the spermatozoa) were run as negative controls. A positive control (EGF-stimulated A231 cell lysate containing EGF receptor, 5 μg) was also included (lane 1). The apparent molecular masses of prestained markers are shown to the left of the blot, and the major 95- and 80-kDa epitopes are labeled on the right of the blot. (B) Histogram of the relative intensities of the bands identified in Fig. 1A and four similar experiments. The increase in the relative intensity (background-subtracted integrated optical density, in pixels) of each band compared to the noncapacitated sample is presented (mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 5). The results from the samples incubated in the presence of C. trachomatis were compared with those from the samples incubated under capacitating conditions in the absence of C. trachomatis by one-way ANOVA. ∗∗∗, significantly different from capacitated spermatozoa (P < 0.001); ∗∗, significantly different from capacitated spermatozoa (P < 0.01); NS, not significantly different from capacitated spermatozoa (P > 0.05).