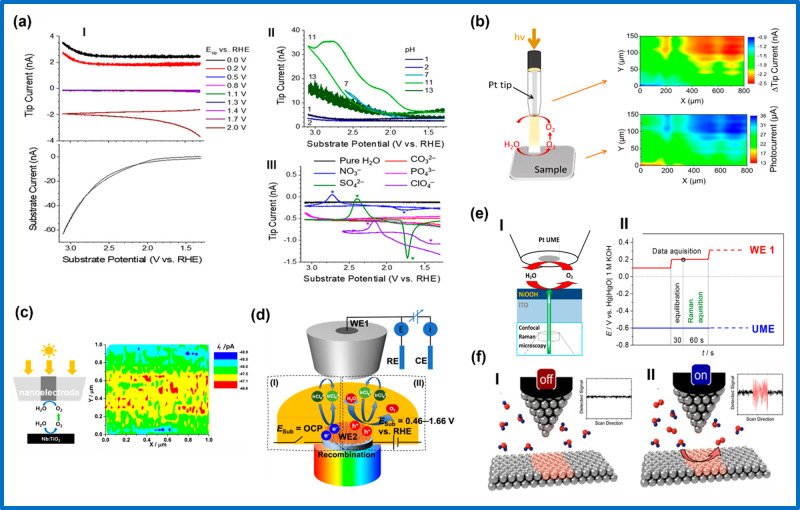
Figure 5.
(a) SG-TC-SECM experiments with a BDD electrode during water oxidation: tip current responses at different tip potentials (top) corresponding to evolved products during voltammetric sweeps of the BDD substrate (bottom) (I). The electrolyte was 0.1 M sulfate, pH 2; the scan rate was 50 mV/s. Comparison of tip currents in 0.1 M sulfate electrolyte at various pH values with the tip biased to reduce oxygen at 0.0 V vs RHE (II). Comparison of collection currents in pure water and 0.1 M electrolyte, buffered at pH 11 for various electrolytes containing different anions. The tip was biased to collect ROS to 1.4 V vs RHE. Asterisks denote features on cathodic and anodic substrate scans (III). Reproduced with permission from ref (460). Copyright 2019 John Wiley and Sons. (b) Scheme of the through-tip illumination approach to perform SPECM experiments with high resolution. Reproduced from ref (196). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society (c) Scheme of SG-TC-SECM to study the photoelectrochemical water oxidation at Nb-doped TiO2 under through tip illumination (left), SECM OER reactivity map of a specific area of the 0.5% doped Nb:TiO2 crystal in a 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7). ETip = −0.9 V; ES = 0 V vs Hg/HgSO4 (right). Reproduced from ref (199). Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society (d) Schematic of the investigation of potential-dependent interfacial charge-transfer kinetics of PEC water oxidation at TiO2 nanorods using SECM: reduction of IrCl62– by photogenerated electrons at OCP (I); simultaneous oxidation of water and IrCl63– by photogenerated holes when ESub = 0.46–1.66 V (vs RHE) (II). Reproduced from ref (461). Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (e) Scheme of the SG-TC-SECM combined with Raman data acquisition (left) and potential profile where the UME is held at a constant potential (−0.6 V) while the sample electrode (WE1) is modulated with discrete potential steps in the positive direction. Reproduced from ref (462). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. (f) Scheme depicting the principle of n-EC-STM. (I) Without a reaction occurring (“off”) the EC-STM signal is stable. (II) An ongoing reaction (‘‘on”) will increase the noise level of the STM signal. The noise is most distinct when the tip is placed over an active site compared to an inactive site. Reproduced with permission from ref (463). Copyright 2021 Elsevier.