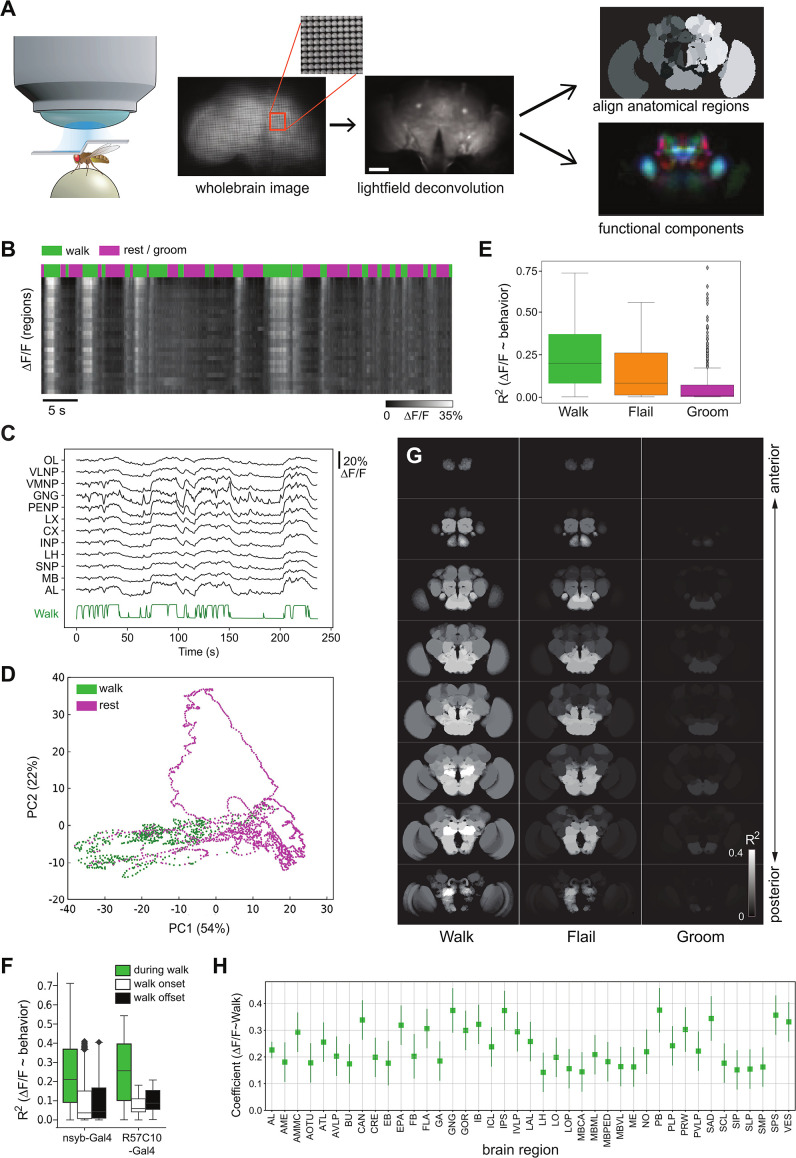
Figure 1. Global brain activation during walk.
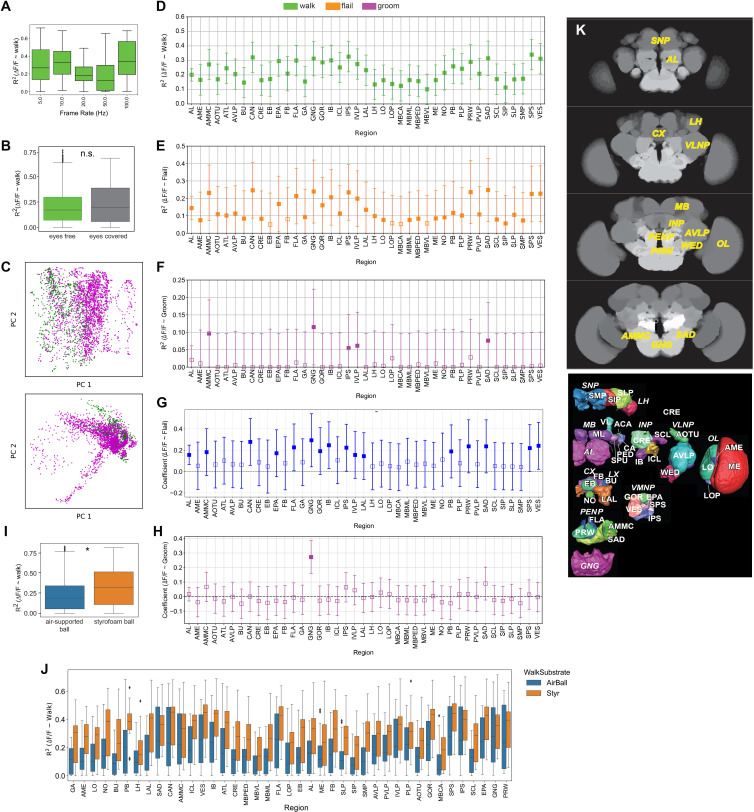
(A) Schematic overview of the preparation and analysis method. Please see methods for details. (B) Raster plot of the activity of regions. Top panels depict walking bouts in green and rest or grooming in magenta. Lower panel shows calcium activity elicited throughout the experiment. The brighter the higher the calcium transients. Mean forward speed: 5.6 mm/s, mean angular velocity: 0.4 rad/s. Bar is 60 μm. (C) Sample traces (ΔF/F) for different brain regions relative to walk (green). (D) First two principal components from whole brain activity color coded with behavior (see additional examples in Figure 1—figure supplement 1). (E) R2 for regression of single regions with single behaviors (all regions were pooled, but p-values are obtained after averaging regions for each fly. Walk: N = 16, Flail: N = 7, Groom: N = 6). Mann–Whitney U-test Bonferroni adjusted p-values: Walk vs. Flail: 0.085, Walk vs. Groom: 0.011, Flail vs. Groom: 0.26. Center line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, ×1.5 interquartile range; points, outliers. (F) R2 of single region activity regression with walk, walk onset and walk offset (all regions were pooled, nsyb-Gal4: N = 16, GMR57C10-Gal4: N = 4). Regressors for walk onset or offset are Dirac functions convolved with the GCaMP response (see Methods). Box plots show: center line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, ×1.5 interquartile range; points, outliers. Mann–Whitney U-test for the two genotypes grouped (comparison of fly-wise averages): walk vs. walk onset: p = 3 × 10−5, walk vs. walk offset: p = 6 × 10−5. (G) Z-stack map of R2 median (Walk: N (flies) = 16, Flail: N = 7, Groom: N = 6) for regression between single region activity and walk, flail or groom (see values in Figure 1—figure supplement 1D-F). (H) Coefficient of single region’ activity regression with walk. All regions’ 95% CI ( bars) are above zero and all adjusted p-values <0.001 (Benjamini–Hochberg correction). N = 16.