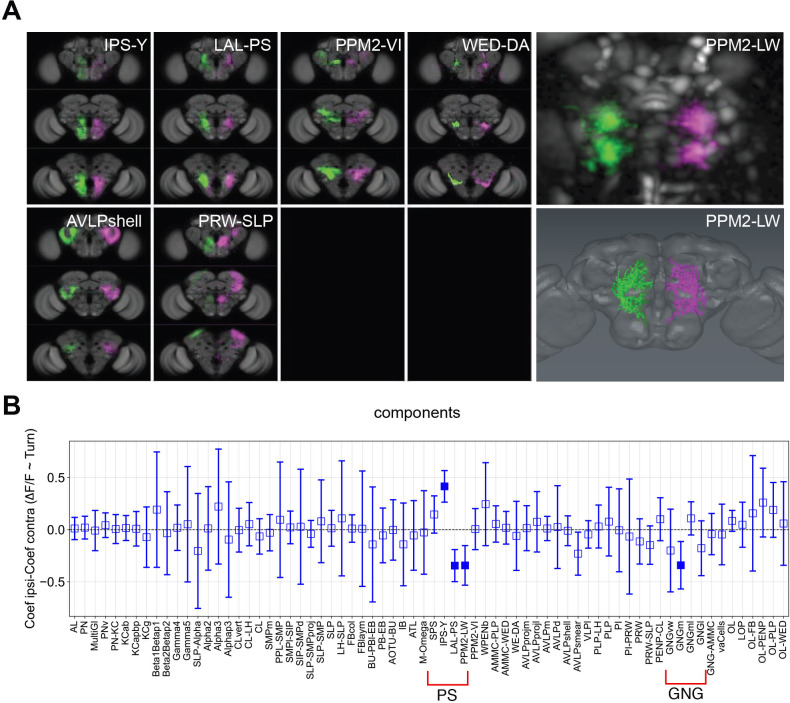
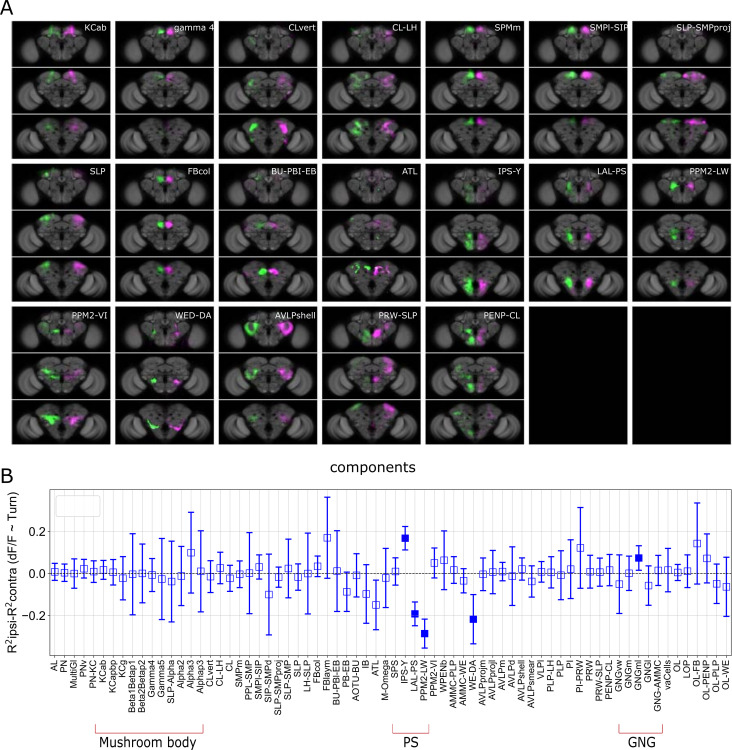
Figure 5. Turning activates specific components and candidate neurons.
(A) Examples of components present in both the left and right hemispheres labeled in different colors (magenta and green). Panels on the right present an example component that could be mapped to a single neuron. Upper right panel: Turning-correlated component, lower right panel: reconstruction of neuron that this functional component was mapped to. (B) Difference between the correlation coefficient (normalized ∆F/F) for turning on the ipsilateral side and the coefficient on the contralateral side is displayed as a function of the identified components. Positive and negative correlations correspond to components being active more during turn on the ipsilateral side than the contralateral side and the reverse, respectively. See Table 2 for definition of acronyms. N = 58 flies of different genotypes, see table in methods for details. Empty markers correspond to adjusted (Benjamini–Hochberg correction) p-value >0.05 for comparison to 0. Bars are 95% CI.