Abstract
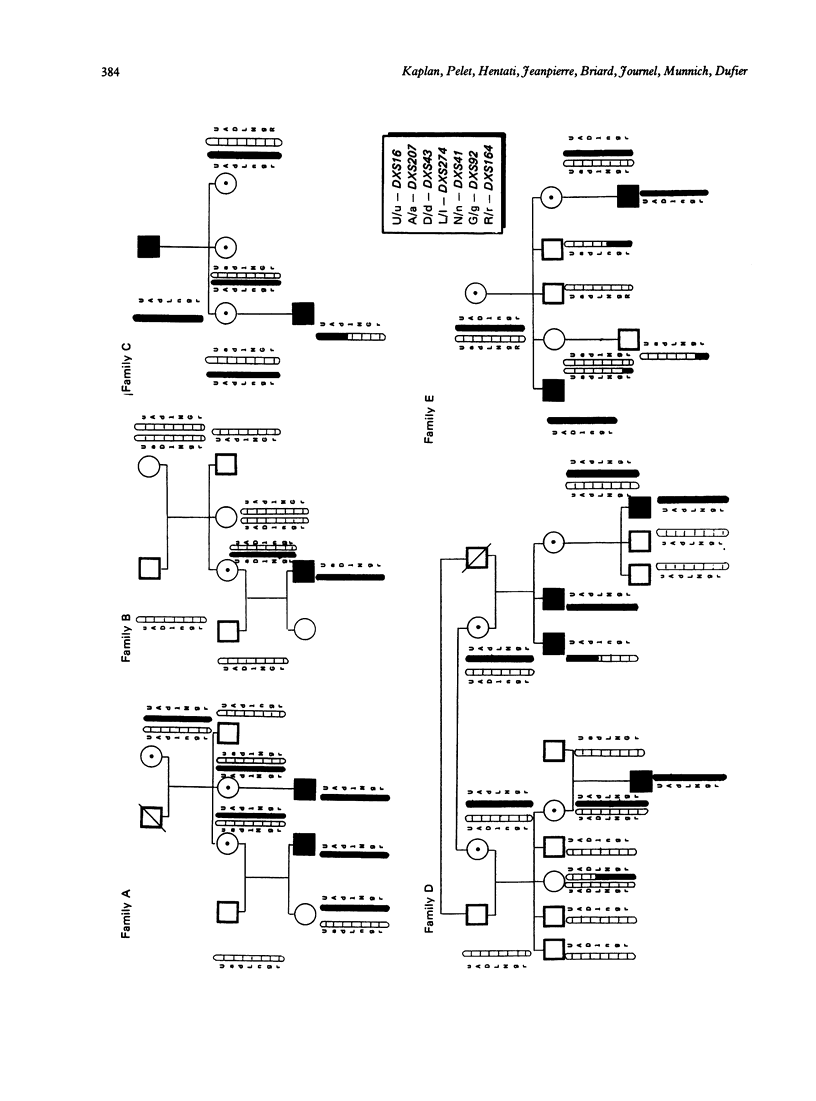
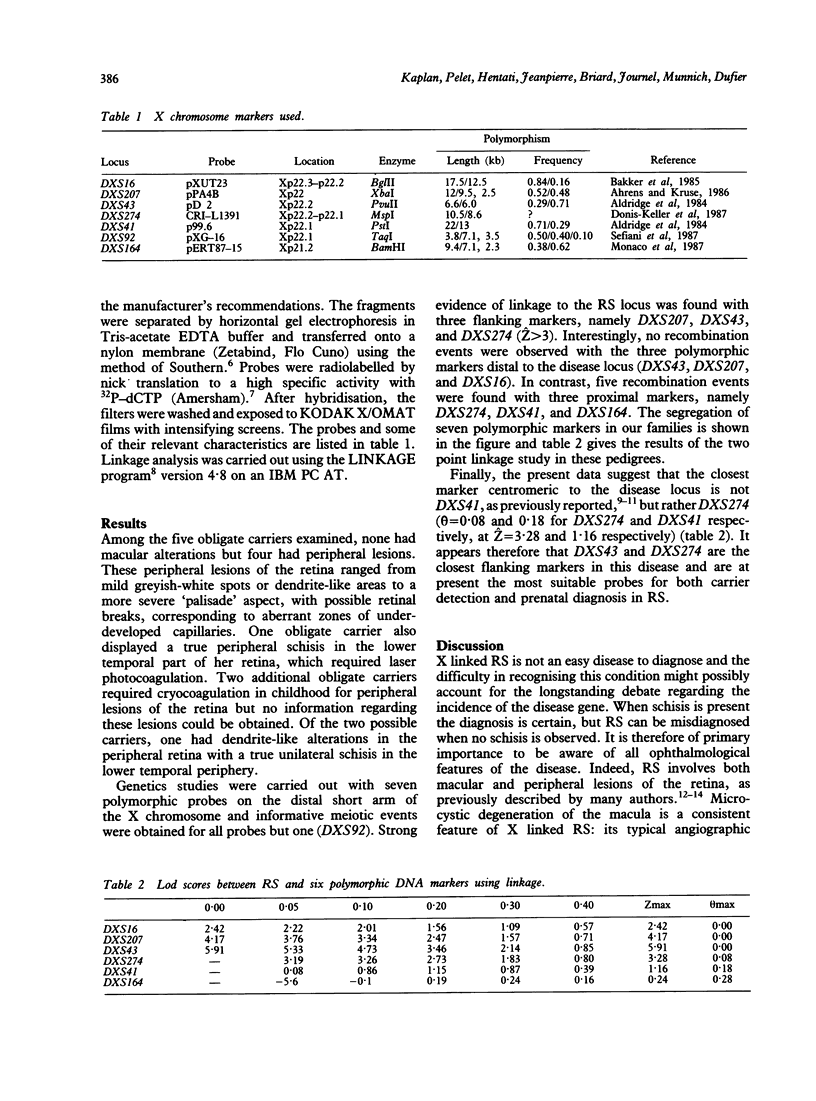
X linked retinoschisis (RS) is a vitreoretinal disease resulting from microcystic degeneration of the macula associated with peripheral lesions. The disease gene has already been assigned to the distal short arm of the X chromosome (Xp22.2) by linkage studies. In order to contribute both to a better localisation of the RS locus and to genetic counselling in RS families, we have carried out a clinical and genetic analysis in seven pedigrees. We show, first, that in contrast with previous reports, heterozygote carriers frequently express the disease, and display peripheral retinal alterations similar to those found in affected males. Second, while distal markers DXS16, DXS207, and DXS43 are closely linked to the disease locus, a high level of recombination events was found with centromeric markers, namely DXS274, DXS41, and DXS164. These findings must be taken into account for both carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis in X linked RS.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo T., Forsius H., Kärnä J., Frants R. R., Eriksson A. W., Wood S., Kruse T. A., de la Chapelle A. Linkage relationships and gene order around the locus for X-linked retinoschisis. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;43(4):476–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo T., Kärnä J., Forsius H., de la Chapelle A. X-linked retinoschisis is closely linked to DXS41 and DXS16 but not DXS85. Clin Genet. 1987 Sep;32(3):192–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1987.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALIAN J. V., FALLS H. F. Congenital vascular veils in the vitreous; hereditary retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1960 Jan;63:92–101. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1960.00950020094014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Goonewardena P., Chotai J., Anvret M., Pettersson U. DNA linkage analysis of X-linked retinoschisis. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):228–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00291666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl N., Pettersson U. Use of linked DNA probes for carrier detection and diagnosis of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Oct;106(10):1414–1416. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140578026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber J. P., Weidinger S., Goedde H. W., Ole K. The deficient alpha-I-antitrypsin phenotype PI P is associated with an A-to-T transversion in exon III of the gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;45(1):161–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsius H., Eriksson A., Nuutila A., Vainio-Mattila B., Krause U. A genetic study of three rare retinal disorders: dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, x-chromosomal retinoschisis and grouped pigments of the retina. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Mar;7(3):83–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert G., Peterson J., Krawczak M., Zoll B. Linkage relationship between retinoschisis and four marker loci. Hum Genet. 1988 Aug;79(4):382–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00282183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Alembik Y., Gilgenkrantz S., Mujica P., Nivelon-Chevallier A., Pembrey M. E., Young I. D., Mandel J. L. Probable localisation of the Coffin-Lowry locus in Xp22.2-p22.1 by multipoint linkage analysis. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):523–530. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvanet-Bouccara A., Galaup A. Rétinoschisis juvénile idiopathique des jeunes gens. J Fr Ophtalmol. 1983;6(5):487–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wienker T. F., Dallapiccola B., Bender K., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Linkage relationships between Retinoschisis, Xg, and a cloned DNA sequence from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):143–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00327111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


