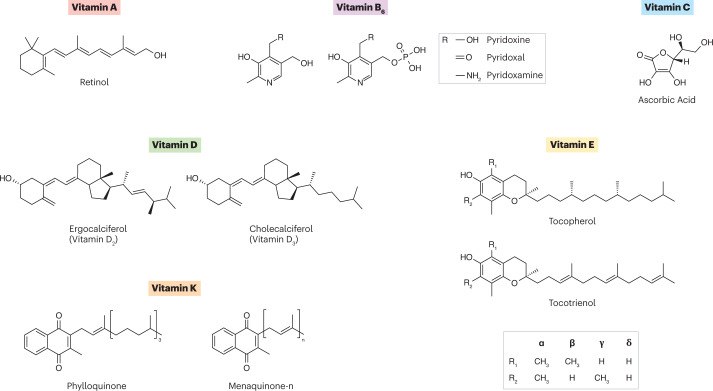
Fig. 2. Structures of vitamins discussed in this Perspective.
Vitamin A (all-trans retinol) contains a β-ionone ring with an isoprenoid side chain and a hydroxyl functional group. Vitamin B6 is the generic name for six vitamers defined based on the R group and phosphorylation status. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) weakly resembles a cyclic sugar molecule. Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) structures are defined as secosteroids. Vitamin E contains four tocopherols and four tocotrienols that are assigned the Greek letters α, β, γ and δ based on the functional group in R1 and R2. Vitamin K structures have a characteristic 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone structure and a unique side chain. Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) has a phytyl side chain and vitamin K2 (menaquinone) has a polyisoprenyl side chain.