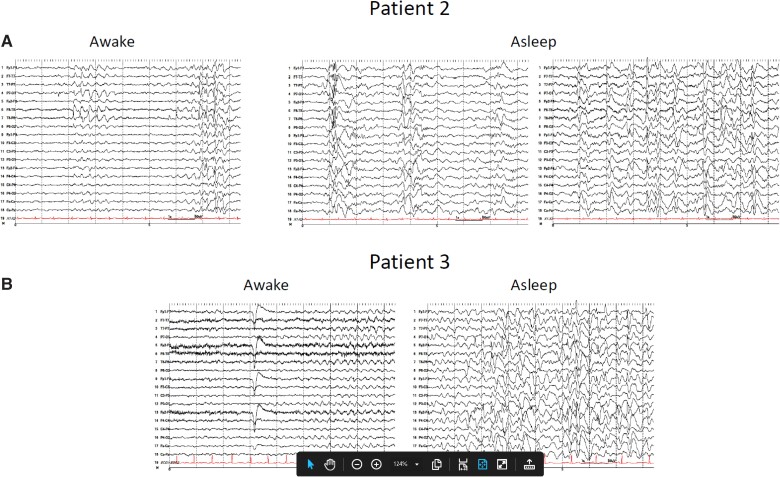
Figure 2.
EEG recordings including sleep in patients with nodding syndrome. Patients underwent long-term EEG monitoring with a 27-channel digital EEG with time-locked video and single-lead EKG. The EEG electrodes were placed according to the internationally accepted 10–20 system of electrode placement. In addition, subtemporal F9, F10, T9, T10, P9 and P10 electrodes were placed for better localization. The EEG events were reviewed with at least three standard montages. (A) Interictal EEG performed on Patient 2 while awake (left) shows slow background activity with superimposed focal slowing and sharp waves in the temporal regions, at times becoming more diffuse. While asleep (right), generalized and multifocal spikes and polyspike and wave activity are present, frequently embedded within K complexes. (B) Interictal EEG performed on Patient 3 while awake (left) shows diffuse background slowing, at times with runs of semirhythmic or rhythmic theta activity. While asleep (right), findings similar to Patient 2 are observed.