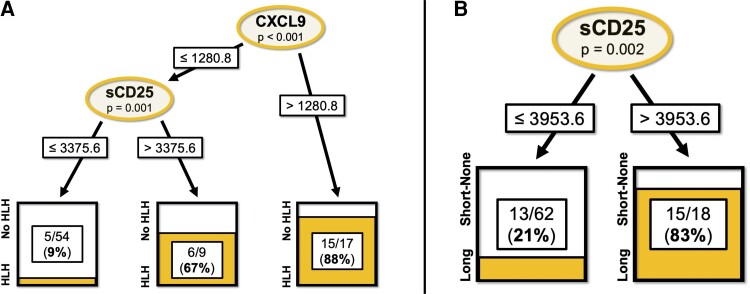
Figure 3.
Decision-tree analyses predicting (A) HLH-IRIS and (B) prolonged (>8 weeks) corticosteroid course at the IRIS time point. Decision trees were constructed using 12 biomarkers (IFNγ, CXCL9, CXCL10, IL-18, IL-18BP, sCD25, CD163, IL-6, CRP, IL-10, IL-27, C1q) and 2 clinical laboratory tests (ferritin, hemoglobin) with the R “ctree” package (version 4.1.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing). Potential splits are only included in the tree model if they met the Bonferroni-adjusted P value for statistical significance (P < .05). Ovals indicate a split in the prediction rule on a specific variable, along with the corresponding P value. Each rectangle shows the percentage of observations within that branch that met the outcome variable. The binary outcomes of HLH versus no HLH and steroids >8 weeks (Long) versus steroids <8 weeks or no steroids (Short-None) were evaluated. Biomarker values are represented as pg/mL. Abbreviations: BP, binding protein; CRP, C-reactive protein; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; Hgb, hemoglobin; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; IFNγ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; IRIS, immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; sCD25, soluble CD25.