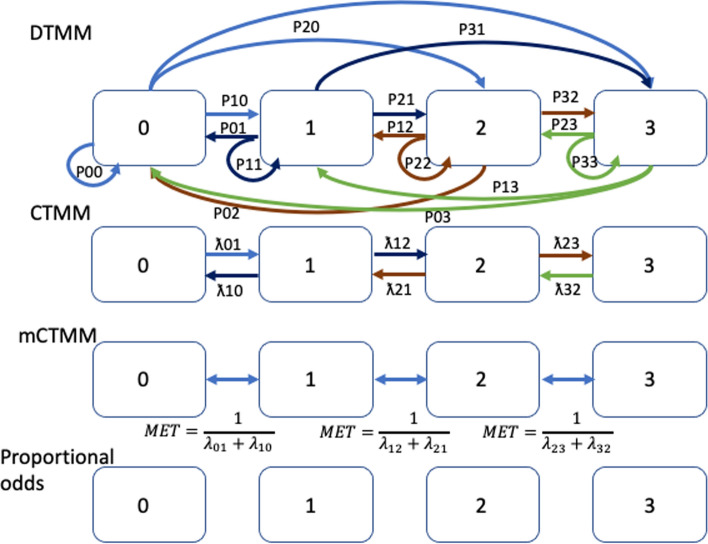
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of different Markov models and proportional odds model adapted from Schindler et al. [44]. The preference of selection of one type of Markov model vs. others depends upon the frequency of data collection (time interval of events) and a number of categories (states) of the events. DTMM might be preferred when data were collected with uniform time intervals, whereas CTMM might be suitable for data collected with non-uniform time intervals across patients either due to study design or missing observations. CTMM models, in general, have fewer parameters relative to DTMM, as CTMM assumes that the transitions only occur between neighboring states. mCTMM is a simpler version of the CTMM model, in which mean equilibration time (MET) between two succeeding states is assumed to be constant across states