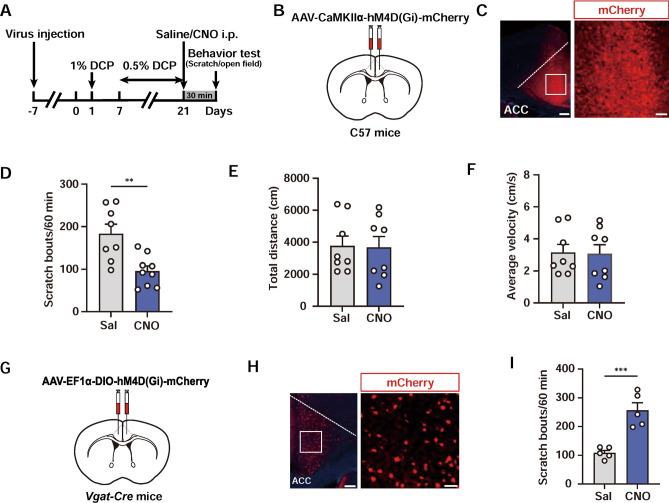
Fig. 2.
ACC modulates chronic itch in a cell type-dependent manner. A Schematic showing the experimental timeline for selective chemogenetic inhibition of excitatory neurons in the ACC. B Scheme for specific infection of excitatory neurons in the ACC with hM4Di. C A representative image illustrating the expression of hM4Di-mCherry in the ACC. Scale bars, 200 μm (left) and 50 μm (right). D Quantitative analyses of the number of scratching bouts within 60 min in mice treated with saline or CNO to chemogenetically inactivate excitatory ACC neurons. n = 8 or 9 mice; **P <0.01; unpaired Student’s t test. E, F Total distance travelled (E) and average velocity (F) in the open field. No significant difference was found between the two groups. n = 8 mice per group. G Scheme for specific infection of inhibitory neurons in the ACC with hM4Di. H Histological verification of viral infection. Scale bars, 200 μm (left) and 50 μm (right). I Chemogenetic suppression of inhibitory neurons in the ACC enhances scratching behaviors in chronic itch. n = 5 mice; ***P <0.001; unpaired Student’s t test. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.