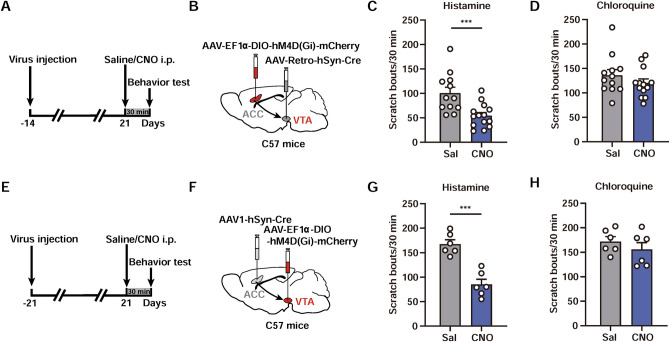
Fig. 6.
The ACC→VTA circuit modulates histaminergic itch sensation. A Experimental timeline for chemogenetic suppression of VTA-projecting ACC neurons in acute itch. B Scheme for specific infection of VTA-projecting ACC neurons with hM4Di. C, D Chemogenetic inhibition of ACC neurons that project to the VTA causes a significant decrease in histamine- (C) but not chloroquine-evoked (D) scratching behaviors. n = 12–14 mice per group; ***P <0.001; unpaired Student’s t test. E Experimental timeline for the chemogenetic suppression of ACC-innervated VTA neurons in acute itch. F Scheme for specific infection of ACC-recipient VTA neurons with hM4Di. G, H Chemogenetic inhibition of VTA neurons that receive inputs from the ACC strongly attenuates histamine- (G) but not chloroquine-induced (H) scratching behaviors. n = 6 mice per group; ***P <0.001; unpaired Student’s t test. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM.