Fig. 5.
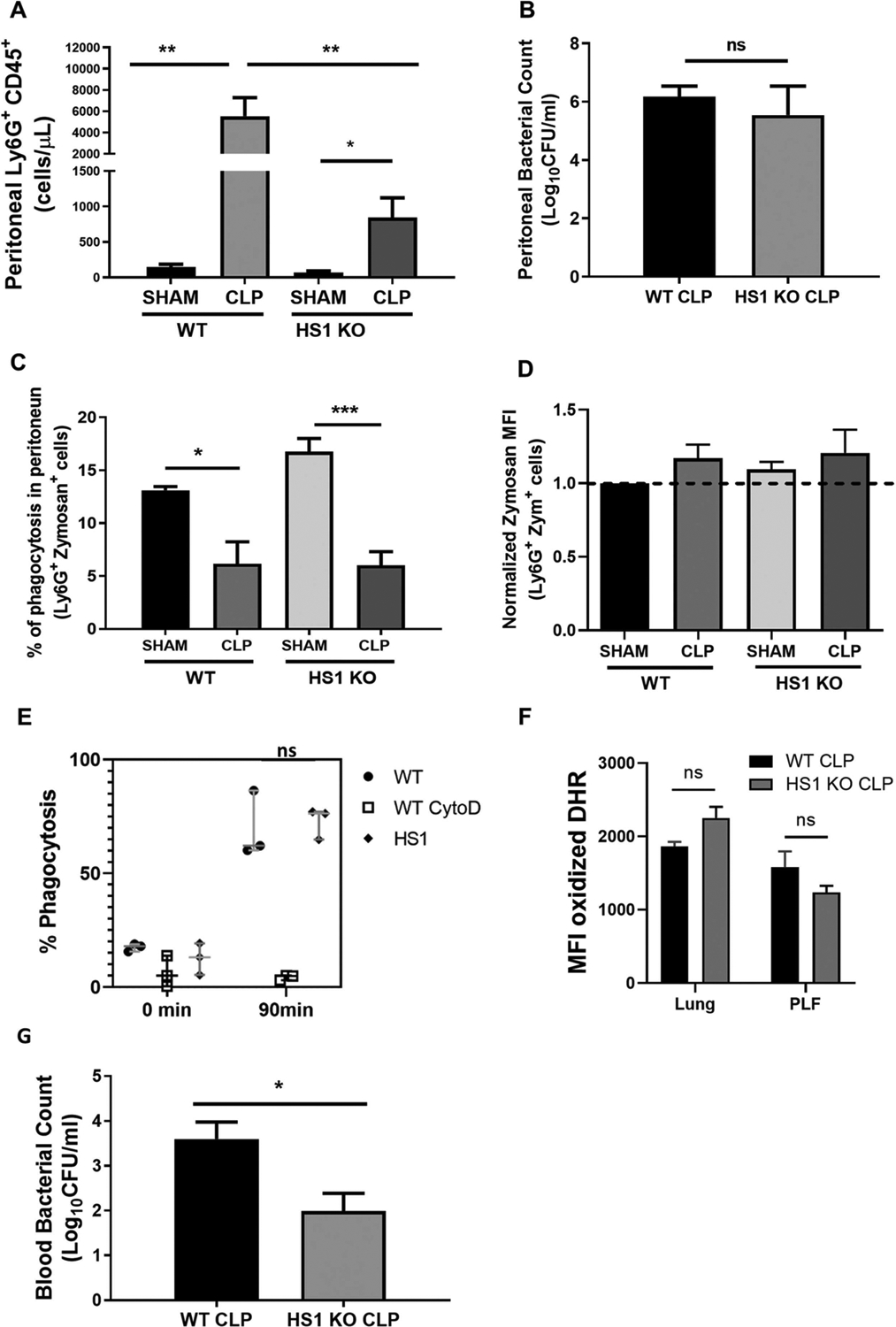
Fewer neutrophils infiltrate the peritoneum in CLP-induced sepsis in the absence of HS1. (A) Frequency of Ly6G+CD45+ cells in the peritoneum 24 h after CLP. (B) Peritoneal bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) were determined 24 h post-CLP by inoculating peritoneal lavage fluid on tryptic soy agar and counting CFU after 24 h. (C) Frequency of Ly6G+CD45+ cells that phagocytosed zymosan particles after 25 min incubation in the peritoneum 24 h post-CLP. (D) Zymosan mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) in Ly6G+ neutrophils (n = 7 in A-D). (E) Frequency of HoxB8 neutrophils that phagocytosed pHrodo Green S. aureus after 90 min incubation. Cytochalasin D treatment as control prevented phagocytosis (n = 3 independent experiments in triplicate). (F) Production of reactive oxygen species as determined by DHR assays is not significantly affected in the absence of HS1 in lung neutrophils and neutrophils from PLF. (G) Bacterial CFU in the peripheral blood (PB) of septic WT and HS1-KO mice (n = 5–8). Data are displayed as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, non-significant; PLF, Peritoneal Lavage Fluid; zym, zymosan.
