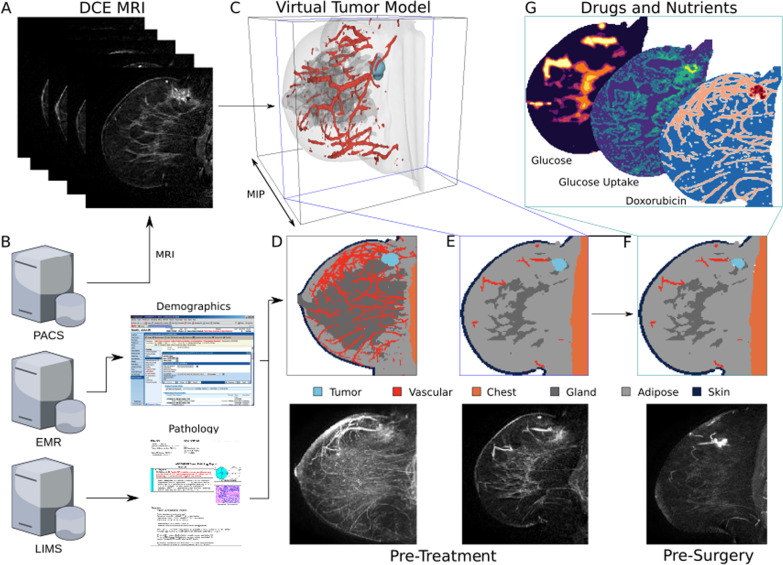
Fig. 2.
TumorScope Predict model. A DCE-MRI imaging data form the basis of a patient’s virtual tumor via a deep learning-based segmentation model that classifies each voxel as comprising primarily tumor, vascular, fibroglandular, adipose, skin, and chest “tissues”. B Along with imaging data extracted from the hospital’s PACS server, a patient’s demographic and pathology data are extracted from the EMR and LIMS servers, respectively, to create a unique profile of the tumor biology in the virtual tumor. C A rendering of a 3D virtual tumor model for a patient is shown, along with a comparison of the pre-treatment segmentation with the MRI as MIPs through the volumes (D) and as slices through the 3D volume at the point of greatest tumor area (E). The virtual tumor model is input into the TS simulation engine, which simulates the response to treatment longitudinally throughout treatment to the surgery date. This pre-surgery data can be compared directly to MRIs taken for surgery planning (F). G The TS platform simulates the spatial gradients of important drugs and nutrients, and how the tumor dynamically responds to them, capturing drivers of response