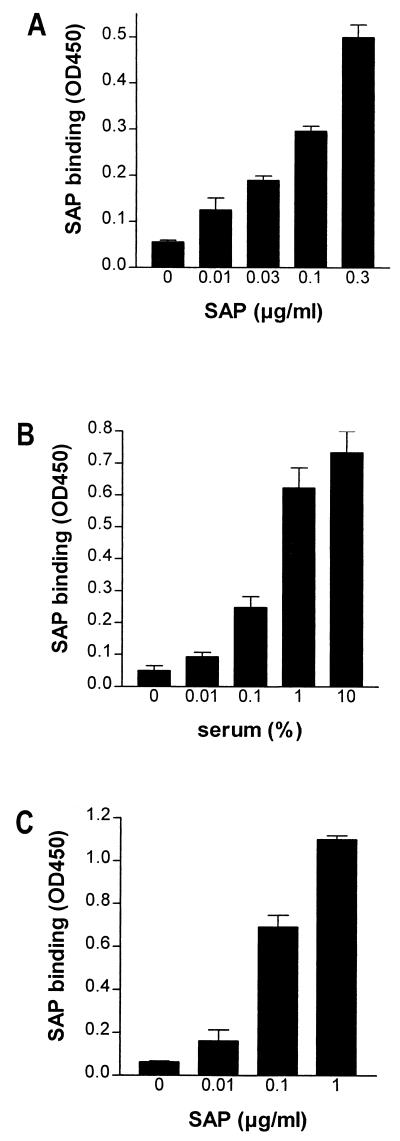
FIG. 4.
SAP binds to HDL and ApoAI. The binding of SAP was tested with isolated HDL (A), HDL in serum (B), and purified ApoAI (C). (A) For the binding of SAP to isolated HDL, HDL (3 μg/ml) was used to coat a microtiter plate overnight. After washing, increasing concentrations of SAP were tested for binding, as detected by a biotinylated anti-human SAP MAb and subsequent peroxidase-labeled streptavidin. (B) The binding of SAP to HDL in serum was tested by incubating serum in an anti-human SAP MAb-coated microtiter plate, followed by the detection of captured HDL with a polyclonal anti-human ApoAI antibody and a peroxidase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG. (C) The binding of SAP to ApoAI was tested by incubating increasing concentrations of SAP in an ApoAI-coated microtiter plate and detecting SAP binding as described above. Data represent the mean OD450 ± SEM of two (A and C) and three (B) separate experiments.