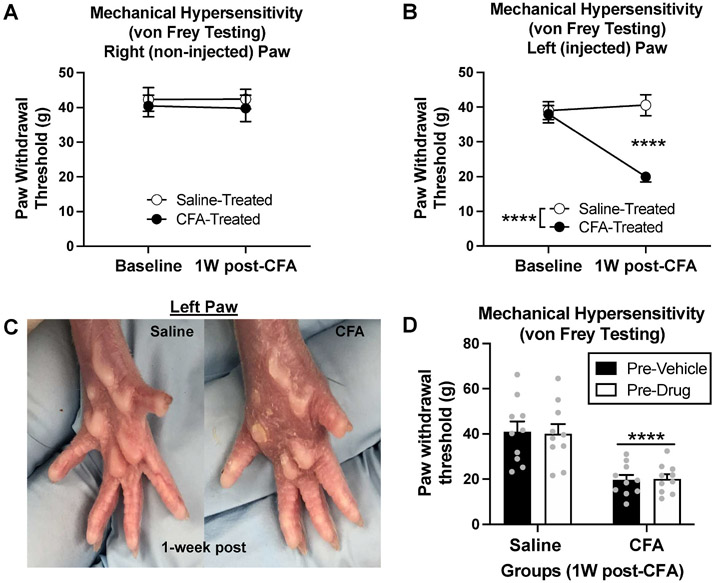
Fig. 2. Experiment 1: Effects of CFA on mechanical hypersensitivity in rats.
(A) There was no effect of CFA treatment or time on paw withdrawal thresholds in the right (non-injected) hindpaw (p > 0.05). (B) At one week, CFA animals demonstrated a decrease in paw withdrawal thresholds from baseline (****p < 0.0001) and compared to saline controls (****p < 0.0001), indicating mechanical hypersensitivity. (C) One-week post-injection, CFA treatment produces visually evident inflammation in the left (injected) hindpaw compared to the left hindpaw of saline-injected controls. (D) Rats were split into four groups based on one week paw withdrawal thresholds (left paw). Prior to l-DOPA & pramipexole treatment, there was an effect of CFA treatment (****p < 0.0001), but no difference in drug treatment groups (pre-vehicle vs. pre-drug) (p > 0.05). Bars represent means and symbols represent individual data points.