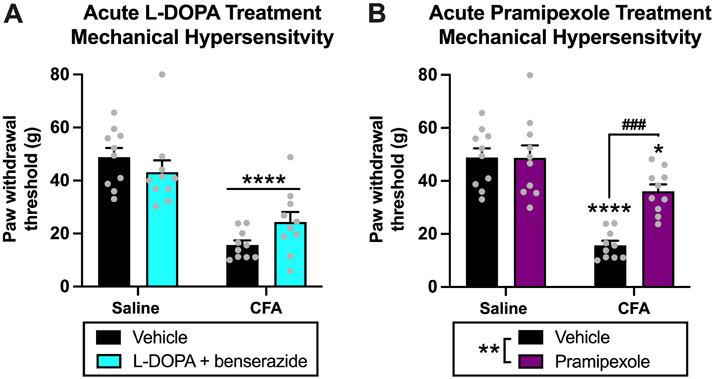
Fig. 3. Experiment 1: Effects of acute dopamine system agonism on mechanical hypersensitivity in rats experiencing chronic inflammatory pain.
(A) For acute l-DOPA treatment, there was an effect of CFA treatment (****p < 0.0001) on paw withdrawal thresholds and an interaction (p < 0.05), but no effect of l-DOPA treatment (p > 0.05). (B) For acute pramipexole treatment, there were effects of CFA treatment (p < 0.0001) and pramipexole treatment (**p < 0.01) on paw withdrawal thresholds, and an interaction (p < 0.001). Post hoc analysis revealed that paw withdrawal thresholds of CFA-vehicle (****p < 0.0001) and CFA-pramipexole (*p < 0.05) animals were decreased compared to saline-vehicle animals. Paw withdrawal thresholds of CFA-pramipexole animals were increased compared to CFA-vehicle animals (###p = 0.001), but there was no difference in paw withdrawal thresholds between saline-vehicle and saline-pramipexole animals (p > 0.05). This demonstrates that acute pramipexole treatment increases paw withdrawal thresholds and reduces mechanical hypersensitivity in CFA animals 1 h after acute administration but produces no analgesic effects in saline animals. Bars represent means and symbols represent individual data points.