Figure 1.
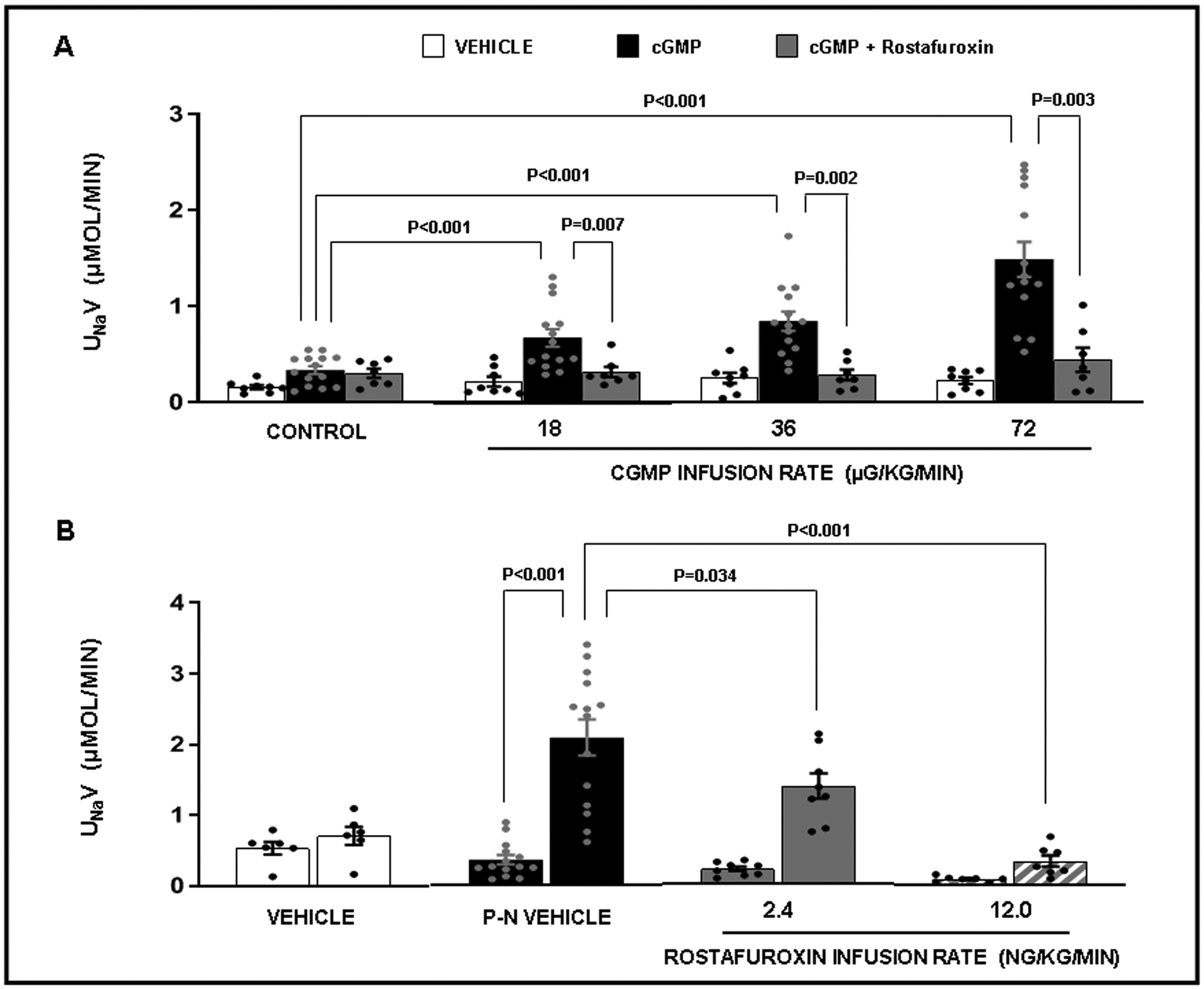
Panel A. Urine sodium (Na+) excretion (UNaV) in response to the following conditions: ( ) Time Control (N=8): rats received renal interstitial (RI) infusion of vehicle (VEH) D5W for the entire 2h study. (
) Time Control (N=8): rats received renal interstitial (RI) infusion of vehicle (VEH) D5W for the entire 2h study. ( ) cGMP (N=14): rats received RI infusion of VEH for 30 min during the control period followed by cumulative RI infusions of cGMP (18, 36, and 72 μg/kg/min; each dose for 30 min) during the experimental periods. (
) cGMP (N=14): rats received RI infusion of VEH for 30 min during the control period followed by cumulative RI infusions of cGMP (18, 36, and 72 μg/kg/min; each dose for 30 min) during the experimental periods. ( ) cGMP + Rostafuroxin (RF) (N=7): rats received RI infusion of VEH for 30 min during the control period followed by the RI co-infusion of cGMP + RF (12 ng/kg/min) during the experimental periods. Results are reported as μmol/min. Panel B. Urine sodium (Na+) excretion (UNaV) in response to the following conditions: (
) cGMP + Rostafuroxin (RF) (N=7): rats received RI infusion of VEH for 30 min during the control period followed by the RI co-infusion of cGMP + RF (12 ng/kg/min) during the experimental periods. Results are reported as μmol/min. Panel B. Urine sodium (Na+) excretion (UNaV) in response to the following conditions: ( ) Vehicle (VEH) Control (N=6): rats received renal interstitial (RI) infusion of VEH D5W during both 30 min periods. (
) Vehicle (VEH) Control (N=6): rats received renal interstitial (RI) infusion of VEH D5W during both 30 min periods. ( ) Pressure-natriuresis (P-N) VEH (N=14): rats received RI infusion of VEH during both the 30 min control and 30 min high renal perfusion pressure periods. (
) Pressure-natriuresis (P-N) VEH (N=14): rats received RI infusion of VEH during both the 30 min control and 30 min high renal perfusion pressure periods. ( ) P-N + Rostafuroxin (RF; 2.4 ng/kg/min) (N=8): rats received RI infusion of RF during both the 30 min control and 30 min high renal perfusion pressure periods. (
) P-N + Rostafuroxin (RF; 2.4 ng/kg/min) (N=8): rats received RI infusion of RF during both the 30 min control and 30 min high renal perfusion pressure periods. ( ) P-N + RF (12 ng/kg/min) (N=7): rats received RI infusion of RF during both the 30 min control and high renal perfusion pressure periods. Results are reported as μmol/min. Statistical significance was determined by using the repeated measures analysis with an unstructured covariance matrix in SAS PROC MIXED program. The ANOVA with permutation P value was based on 2000 permutations of group assignment to individual N values and a repeated measures analysis with an unstructured covariance matrix.
) P-N + RF (12 ng/kg/min) (N=7): rats received RI infusion of RF during both the 30 min control and high renal perfusion pressure periods. Results are reported as μmol/min. Statistical significance was determined by using the repeated measures analysis with an unstructured covariance matrix in SAS PROC MIXED program. The ANOVA with permutation P value was based on 2000 permutations of group assignment to individual N values and a repeated measures analysis with an unstructured covariance matrix.
