FIGURE 14.
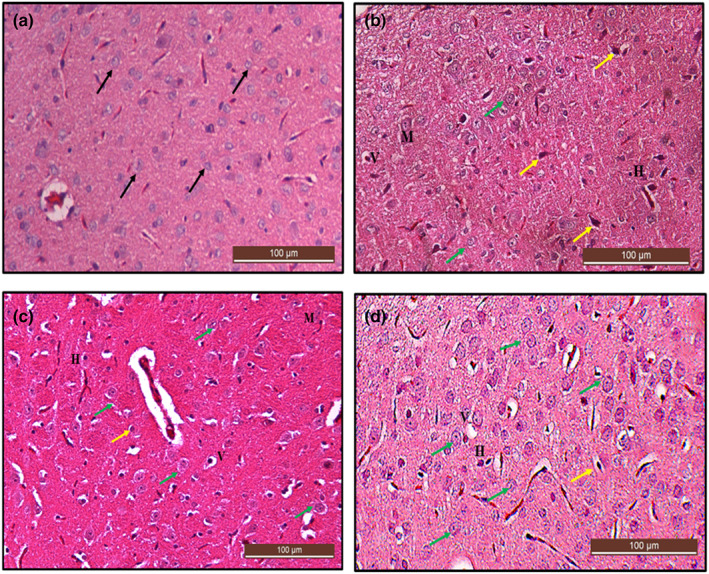
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)‐stained cerebral cortex sections from rats treated with (a) normal saline (control), showing the normal architectural and cellular morphology (black arrow) of the cerebral cortex. (b) 100 mg/kg of curcumin (cur 100) showing some level of cellular degenerations (yellow arrow), irregular‐shaped multipolar (M), and vacuolated neuronal cells (V) with hyperchromatic cells (H). (c) 50 mg/kg of cur‐CSCaCO3NP (cur‐CSCaCO3NP 50) and (d) 100 mg/kg of cur‐CSCaCO3NP (cur‐CSCaCO3NP 100) showing fewer damaged neuronal cells with marked improved normal neuronal cell morphology and very reduced vacuolar spaces around the cells (green arrow). (H&E, ×20, scale bar = 100 μm)
