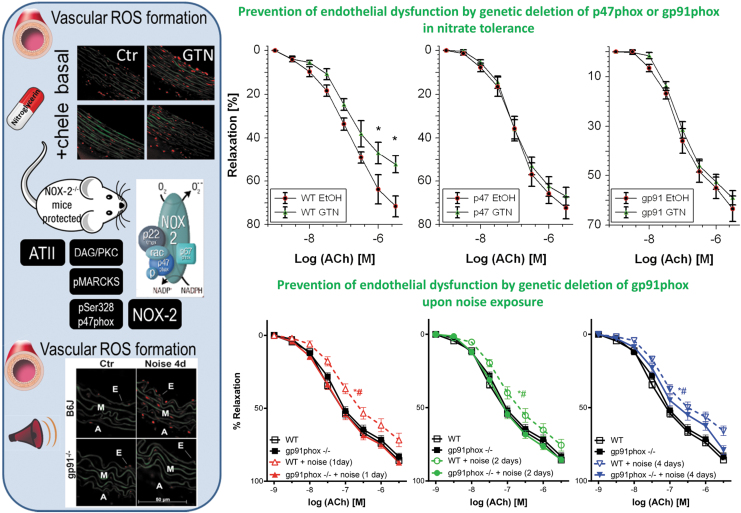
FIG. 4.
Prevention of vascular ROS formation and endothelial dysfunction by GTN or traffic noise exposure by pharmacological or genetic NADPH oxidase inhibition. Left part: Oxidative stress assessed by DHE staining (red fluorescence indicates reactive oxygen species [ROS] formation, whereas green fluorescence represents the autofluorescence of the basal lamina). E=Endothelium, M = Media, A = Adventitia. GTN (50 mg/kg/day for 3.5 days) treatment leads to aortic oxidative stress in rats, which was prevented by the PKC inhibitor chelerythrine (chele) (Knorr et al, 2011). Aircraft noise exposure [72 dB(A) around-the-clock for 1, 2, or 4 days] leads to aortic oxidative stress in rats, which was prevented by genetic deficiency of gp91phox (Kroller-Schon et al, 2018). The phagocytic NADPH oxidase (NOX-2) plays a key role in the pathomechanisms underlying nitrate tolerance and noise exposure-mediated cardiovascular damage. NOX-2 is activated by ATII receptor activation, leading to DAG formation, a strong PKC activator. PKC activation can be envisaged by phosphorylation of its target protein MARCKS. Activated PKC will cause phosphorylation of p47phox at Ser328 leading to translocation of this cytosolic regulator of NOX-2 to the multienzyme membrane complex of gp91phox with subsequent activation of NOX-2 and superoxide formation. Right part: Endothelial dysfunction (impaired ACh-dependent relaxation) by GTN treatment was prevented in mice with genetic deficiency of p47phox or gp91phox (Wenzel et al, 2008). *p < 0.05 versus WT EtOH solvent control group. Endothelial dysfunction by noise exposure was prevented in mice with genetic deficiency of gp91phox (Kroller-Schon et al, 2018). *p < 0.05 versus WT control group and #p < 0.05 versus gp91phox−/− + noise group. Scheme in the left part was adapted from Frenis et al (2021c) with permission [Copyright © 2021 the authors. Open access (CC BY)]. Data in the left part were reproduced from Knorr et al (2011) (for nitrate tolerance) and Kroller-Schon et al (2018) (for noise exposure) with permission. Data in the right part were reproduced from Wenzel et al (2008) (for nitrate tolerance) and Kroller-Schon et al (2018) (for noise exposure) with permission. ACh, acetylcholine; ATII, angiotensin-II; DAG, diacylglycerol; DHE, dihydroethidine; ROS, reactive oxygen species.