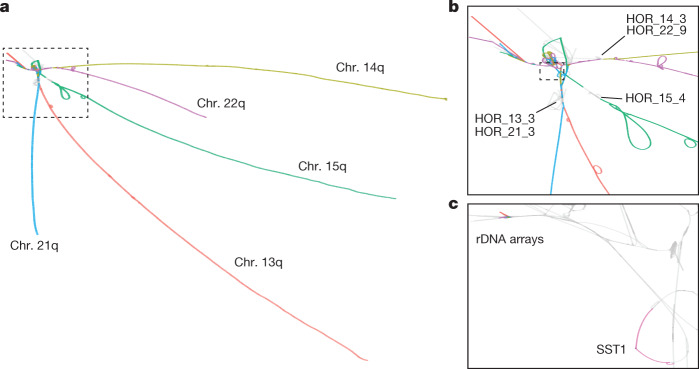
Fig. 2. The acro-PVG derived from the HPRCy1 assembly.
a, The major component of the acro-PVG, shown with nodes in T2T-CHM13 chromosomes labelled with the colour scheme from Fig. 1a. The acrocentric q-arms are almost completely separated, whereas the p-arms unite in a tangle adjacent to the rDNA array. b, A close-up view of the SAAC junction, showing the separation of centromeric high-order repeats of chr. 15 (HOR_15_4) from the other chromosomes, whereas chr. 13 and chr. 21, and chr. 14 and chr. 22 share substantial homology in their arrays, which causes them to collapse in the PVG. A few assemblies span the rDNA array into its distal junction, which presents as a single homologous region across all chromosomes2, and then fray into diverse sequences visible as tips in the top left. c, Closer view of the outlined region in b, focusing on the segmentally duplicated core centred in the SST1 array and the rDNA arrays, as labelled in T2T-CHM13. The highlighted region around the SST1 array is in the same orientation on T2T-CHM13 chr. 13p11.2 and chr. 21p11.2, and is inverted on chr. 14p11.2; these 3 regions have a pairwise identity3 of more than 99%.