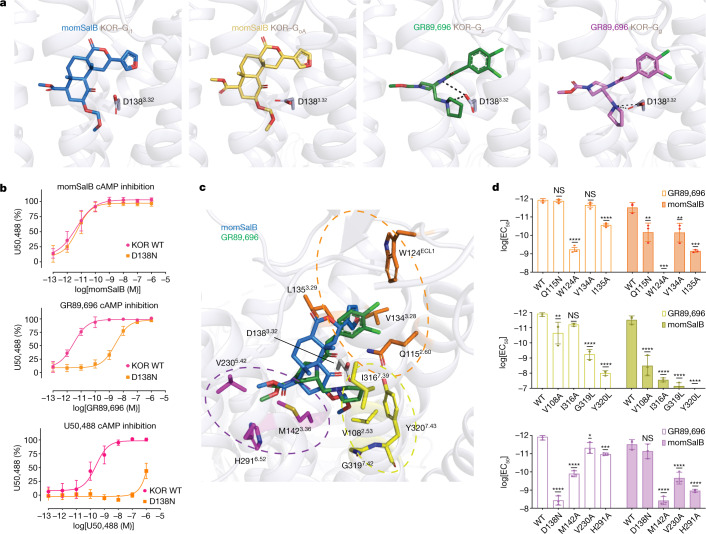
Fig. 2. Ligand-specific interactions with KOR.
a, The binding poses of momSalB and GR89,696 in their respective complex structures. The salt bridge or H-bond interactions in Gz- and Gg-coupled structures are shown as black dashed lines. This salt bridge or H-bond interaction is absent in momSalB-bound KOR. b, The highly conserved anchoring residue Asp1383.32 has a different role in momSalB, GR89,696 or U50,488-mediated KOR activation. Data are normalized to the percentage of the reference agonist U50,488. Data are grouped data ± s.e.m. of n = 3 biological replicates. The full quantification parameters for this experiment are provided in Supplementary Table 1. c, Specific residues in the orthosteric pockets that interact with momSalB or GR89,696. Note that the I1353.29L mutation was included in KOR structure constructs to increase the expression level. d, Mutagenesis screening of binding-pocket residues using G-protein-mediated cAMP inhibition assays. The effect on the potency of momSalB or GR89,696 was quantified on the basis of the log[EC50] values. Data are log[EC50] ± s.e.m. of n = 3 biological replicates. Statistical significance for each mutant was calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test compared with the wild type (WT); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; NS, not significant. GR89,696: P = 0.016 (V230A), P = 0.0008 (H291A), P = 0.1758 (V134A), P = 0.9814 (Q115N), P = 0.006 (V108A), P = 0.1165 (I316A); momSalB: P = 0.344 (D138N), P = 0.0009 (W124A), P = 0.0064 (V134A), P = 0.0068 (Q115N), P = 0.0002 (I135A). The full quantification parameters for this experiment are provided in Supplementary Table 2.