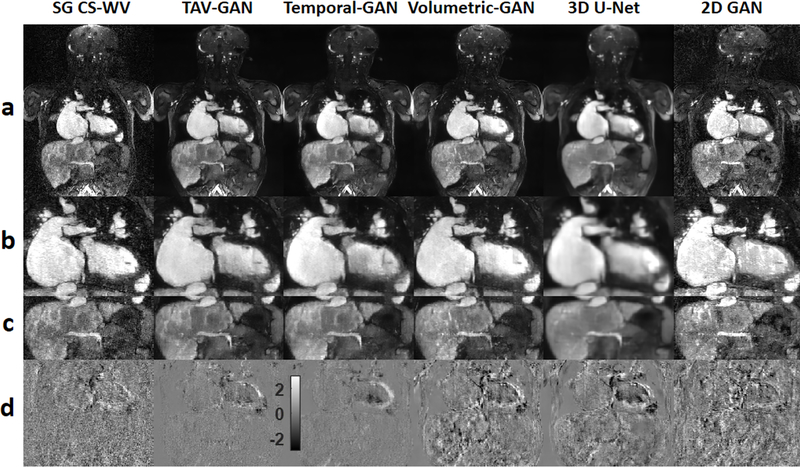
Figure 4.
Qualitative comparison between different image reconstruction methods for a male CHD patient from test dataset B1 (6 y.o. and 18 kg weight) who was scanned under anesthesia. Row (a) shows the reconstruction/respiratory motion correction results and rows (b) and (c) show the zoomed view of the cardiac and liver region. Row (d) shows the temporal difference between 5th and 6th cardiac phases. The 2D-GAN image has substantial residual artifacts. The 3D U-Net image is blurrier than the GAN based methods (TAV-GAN, Temporal-GAN, and Volumetric-GAN). As shown in (d), reconstruction results from TAV-GAN and Temporal-GAN have the lowest incoherency and flickering artifacts, which implies that the proposed TA loss can effectively decrease the temporal incoherency through the cardiac frames. The SG CS-WV was reconstructed based on 5.4X fold under-sampled data; the remaining methods shown were reconstructed based on 14.2X fold under-sampled data.