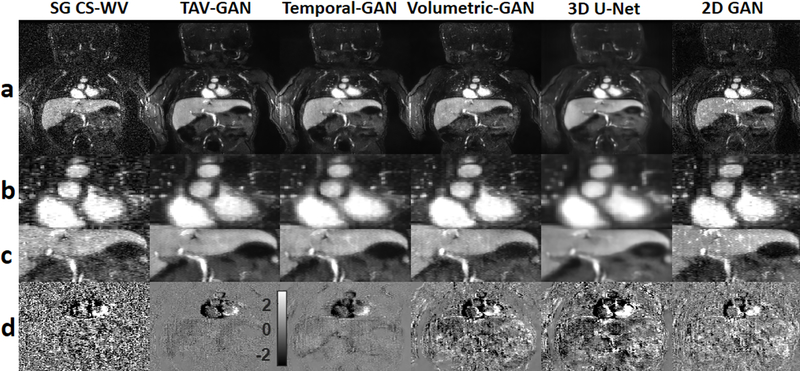
Figure 5.
Qualitative comparison between different methods for a pediatric male patient from test dataset B2 (1 month old and 3.18 kg weight) who was scanned under anesthesia. Rows (a), (b), and (c) show the image reconstruction using 6 different methods and the zoomed view of the cardiac and liver regions. Row (d) shows the temporal difference between 2nd and 3rd cardiac phases. The 2D-GAN image provides the most inferior image quality. The 3D U-Net image was blurrier than the GAN based methods (TAV-GAN, Temporal-GAN, and Volumetric-GAN). The Temporal-GAN image is slightly blurrier than the TAV-GAN and Volumetric-GAN. The reference SG CS-WV image suffers from the residual noise and its quality is inferior to the TAV-GAN and the Temporal-GAN. The SG CS-WV was reconstructed based on 5.7X fold under-sampled data; the remaining methods shown were reconstructed based on 11.4X fold under-sampled data.