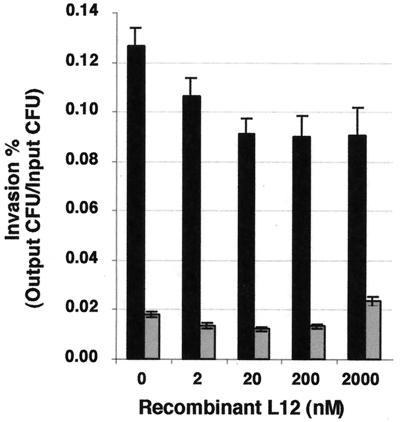
FIG. 7.
Effect of exogenous gonococcal rL12 on GC invasion of Hec1B cells. Various amounts of rL12 were added to Hec1B cells simultaneously with Inv+ GC (black bars) or Inv− GC (gray bars). Invasion is expressed as the percentage of gentamicin-resistant CFU/input CFU. The results are averages of data from triplicate wells from over six experiments. The inhibition of Inv+ GC invasion observed at all concentrations of rL12 and with Inv− GC for rL12 concentrations between 2 and 200 nM is significantly different from the no-rL12 controls (P ≤ 0.005; one-tailed paired Student's t test). At 2,000 nM of rL12, the invasion level of Inv− GC is significantly enhanced over the no-rL12 controls (P < 0.001; one-tailed paired Student's t test). The error bars denote the standard error of the mean.