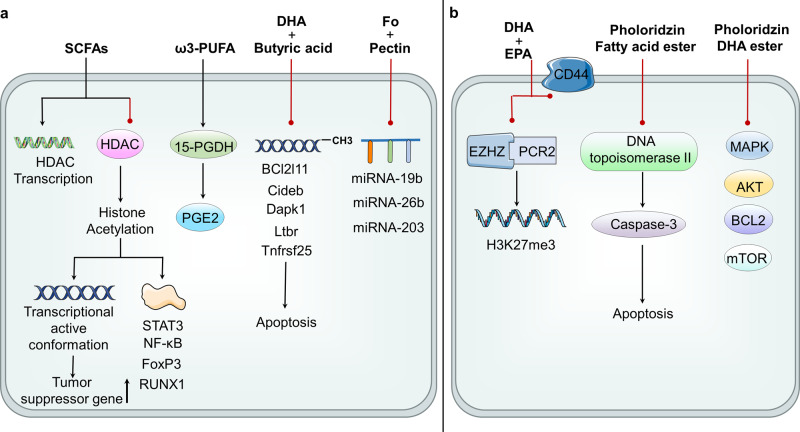
Fig. 3.
Epigenetic regulation of fatty acids and their intermediate metabolites in cancer. ACLY cleaves citrate into oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA, while ACSS connects acetate and CoA to generate acetyl-CoA and generates acetylcholine depot, which together with organic acids affects histone posttranslational modifications and induces Twist2 expression increase. a CRC: SCFAs and ketone bodies inhibit HDAC enzyme to make histone acetylation, up-regulate the tumor suppressor gene, and promote the activation of transcription factors STAT3, NF-kB, FoxP3, N-FAT and RUNX1. It can also directly inhibit the transcription of HDAC gene. ω-3PUFA up-regulates 15 PGDH and catalyzes the oxidation of the 15 (S) -hydroxyl group of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), fish oil and pectin reduce the pro-apoptotic Bcl2l11, Cideb, Dapk1, Ltbr and Tnfrsf25 promoter methylation which promotes cell apoptosis, and down-regulation of miRNA (miRNA-19b, miRNA-26b and miRNA-203). b BCC: DHA and EPA down-regulate the expression of EZH2, and then H3K27me3 modification. Fish oil can down-regulate the expression of CD44, promote ECM remodeling, and inhibit the migration and invasion of cancer cells. DHA inhibits the PPARγ/NF-κB pathway, blocking MMP-9 expression, and triggers exosome secretion of microRNAs that promote angiogenesis genes to inhibit angiogenesis; phloridzin fatty acid esters inhibit DNA topoisomerase IIa activity and activate caspase, inducing apoptosis, Phloridzin’s DHA ester down-regulates BCL2, growth factor receptor and PI3k/AKT/mTOR, Ras/Raf/MAPK and HDAC