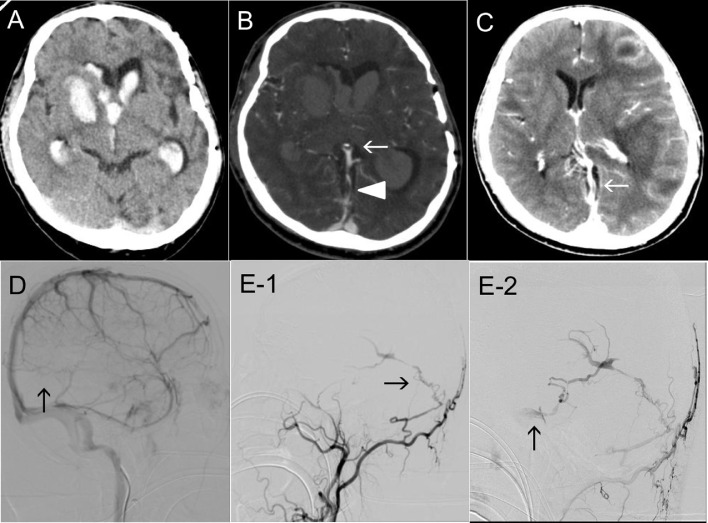
Fig. 1.
(A) Axial CT on admission showing a right putaminal hemorrhage and acute hydrocephalus due to an intraventricular hematoma. (B) Axial CT angiography image showing the bilateral basal vein and the straight sinus (StS) in the arterial phase (arrow), indicating an arteriovenous shunt. Additionally, contrast CT showing a partial defect of the StS (arrowhead), indicating sinus thrombosis. (C) Contrast-enhanced axial CT at the time of multiple brain abscesses 2 years earlier showing patency of the StS (arrow). (D) Venous phase of right ICAG showing StS occlusion (arrow). (E) Left ECAG showing DAVF shunt point from the mastoid branch of the OA to the StS (E-1, arrow). The venous reflux flows to the left cavernous sinus through the basal vein and uncal vein (E-2, arrow) (E-1, E-2: lateral view). CT, computed tomography; DAVF, dural arteriovenous fistula; ECAG, external carotid artery angiography; ICAG, internal carotid artery angiography; OA, occipital artery; StS, straight sinus.