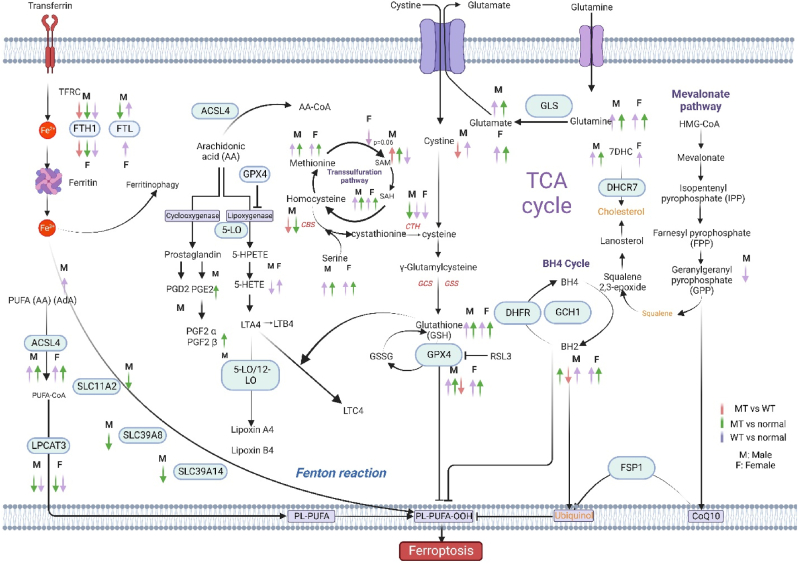
Fig. 5.
Scheme mapping changes to CRC-related metabolites within ferroptotic pathways. Arrows indicate directionality of change in metabolite abundance, color of arrow represents the tissue comparisons: red; KRAS Mutant CRCs compared to KRAS wild type CRCs, green; KRAS mutant CRCs compared to normal colon tissues, purple; KRAS wild type CRCs compared to normal colon tissues. Pathways shown describe the various mechanisms of ferroptosis: Cystine and cysteine availability, uptake through the xCT system or TSP pathway which is essential for GSH synthesis. The decreased accumulation of iron-dependent lipid peroxides by GPX4. The generation of substrates for lipid peroxidation (phospholipids with polyunsaturated acyl tails (PL-PUFAs) by enzymes such as ACSL4 and LPCATs (purple, bottom left) that activate and incorporate free PUFAs into phospholipids. Once PL-PUFAs are incorporated into membrane environments, iron-dependent enzymes and labile iron use molecular oxygen (O2) for peroxidation, generating PL-PUFA-OOH. There are three pathways for eliminating peroxidized PL-PUFAs: the GPX4-glutathione axis the FSP1-CoQ10 axis and the GCH1-BH4 axis. Iron-dependent enzymes including lipoxygenases and cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR) also drive ferroptosis. Labile iron is imported through the transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) and stored in ferritin. Ferritin can be degraded through an autophagy-like process known as ferritinophagy, which releases labile iron and facilitates the peroxidation reaction driving ferroptosis.
Abbreviations: ACSL4, acyl coenzyme A synthetase long-chain family member 4; BH2, dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CoA, coenzyme A; Fe, iron; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GCH1, GTP Cyclohydrolase 1; GCS, glutamylcysteine synthetase; GLS, glutaminase; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH: reduced glutathione, GSSG: oxidized glutathione, GSS, glutathione synthetase; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; NRF2, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; PE, piperazine erastin; PL, phospholipid; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; LPCAT, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids, MUFA, Monounsaturated fatty acids; TFRC, Transferrin Receptor; PGD2, Prostaglandin D2; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; PGF2α, Prostaglandin F2α; PGF2β, Prostaglandin FF2β; LTA4, Leukotriene A4; LTB4, Leukotriene B4; LTC4, Leukotriene C4; SAM, S-Adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-Adenosylhomocysteine; DHFR, Dihydrofolate reductase; DHCR7, 7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase; AA, Arachidonic acid; AdA: Adrenic acid.