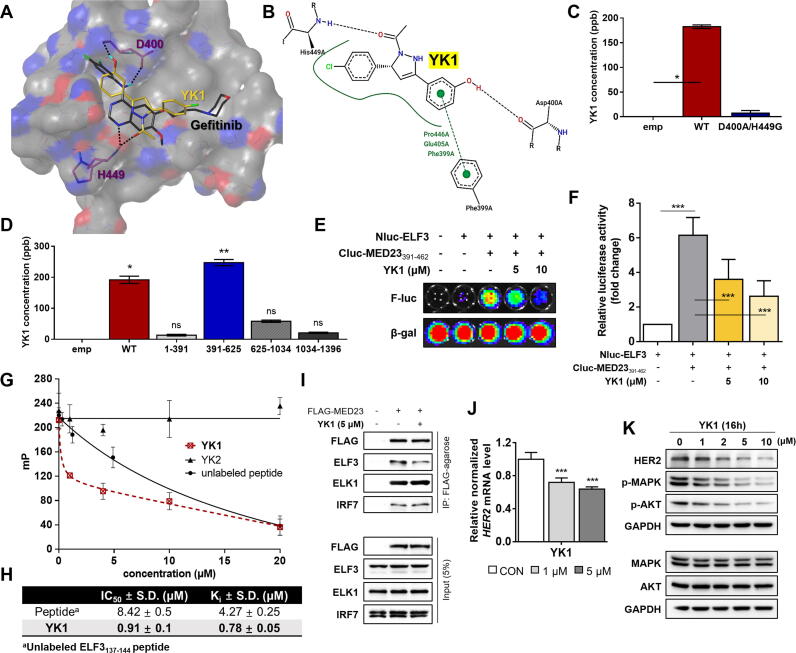
Fig. 3.
Small molecule-aided confirmation of key residues of MED23 in ELF3-MED23 PPI and discovery of YK1 as a specific tool for blocking ELF3-MED23 PPI. (A) Binding orientations of gefitinib and YK1 were compared by overlaying the final docking poses of gefitinib and YK1. MOLCAD hydrogen bonding surface was shown to visualize the distribution of hydrogen bond donors (red) and acceptors (blue). (B) 2D interaction diagrams of the docking model of YK1 was generated through PoseView (https://proteins.plus). Strong π-contacts with F399 along with specific H-bonding to D400 and H449 of MED23 were observed. (C) LC-MS/MS analysis result confirmed direct binding between MED23WT and YK1 via H-bonds with D400 and H449 residues. Binding was significantly lost with MED23 D400A/H449G construct. (D) LC-MS/MS analysis assessed YK1 binding affinity toward various MED23 fragments. YK1 specifically interacted with the 391–625 a.a. region of MED23. (E, F) Representative image (E) and quantification result (n = 3) (F) of the luciferase biosensor assay conducted using Nluc-ELF3WT and Cluc-MED23391-462 fragment. YK1 was co-administered to the ELF3-MED23391-462 interacting system to confirm its PPI inhibitory activity. (G) The extent of ELF3-MED23 PPI inhibition was assessed by the decreased fluorescence polarization (mP) values due to the release of FITC-labeled ELF3 peptide complexed with MED23391-582 protein by dose-dependent treatment of YK1 or unlabeled ELF3 peptide. YK2 was used as a negative control. (H) The IC50 and Ki values of YK1 were calculated from the fluorescence polarization assay results. (n = 3, mean ± S.D.). (I) PPI inhibitory activity of YK1 was evaluated against MED23 and its diverse binding partners using immunoprecipitation assay. YK1 specifically blocked the ELF3-MED23 PPI. (J) mRNA levels of HER2 were evaluated by dose-dependent treatment of YK1 (n = 3, mean ± S.D., GAPDH was used as a control for normalization), ANOVA, ***P < 0.001 vs CON. (K) Protein levels of HER2 and HER2-related downstream signal molecules were evaluated with dose-dependent treatment of YK1. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)