Fig. 3: RBS-binding antibodies utilize a diverse repertoire and are susceptible to mutations in Sb.
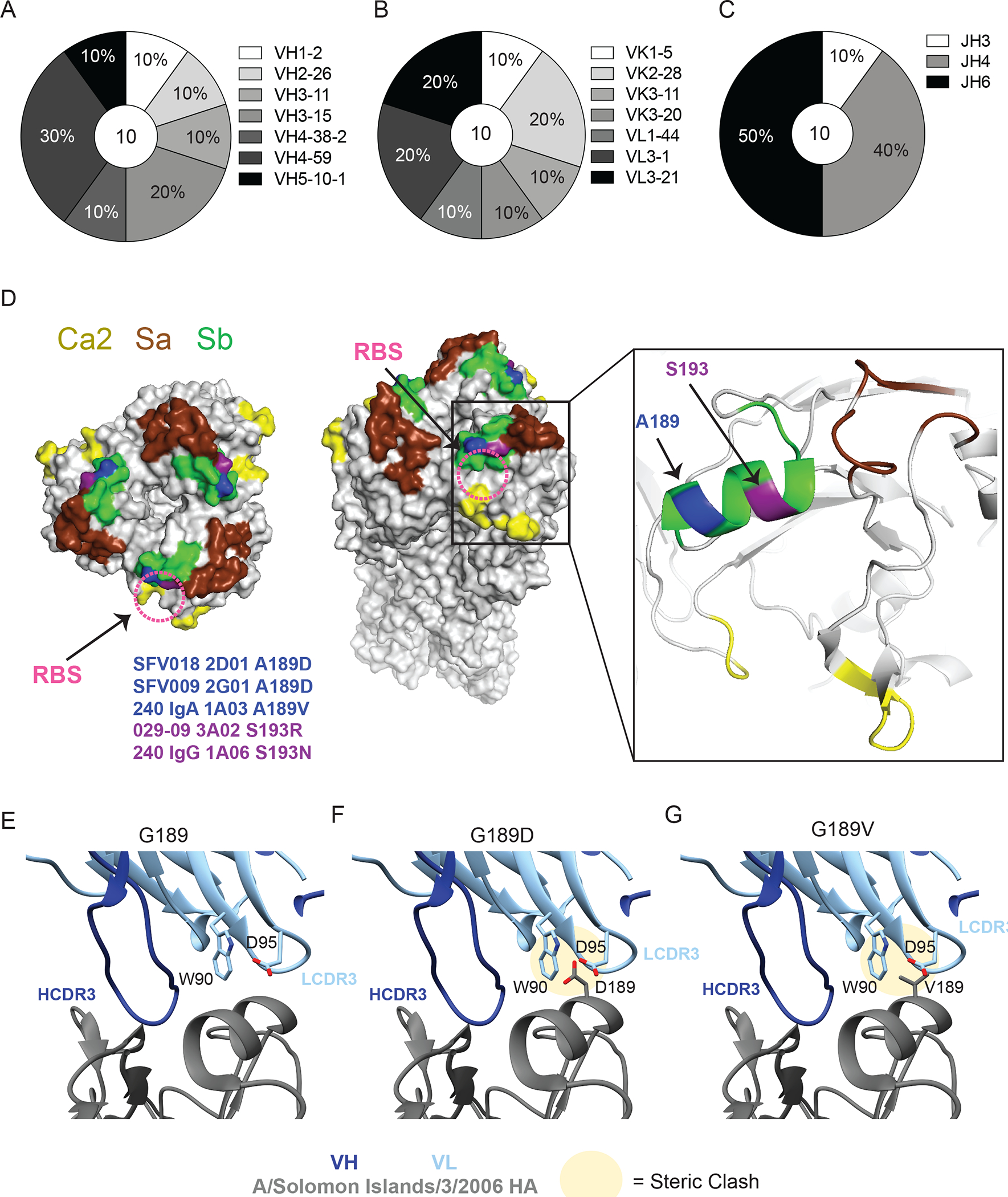
(A-C) Repertoire of unique B cell clones targeting the RBS including VH gene usage (A), VK or VL gene usage (B), and JH gene usage (C). Numbers in center of pie graphs represents number of distinct clones analyzed. (D) Location of virus escape mutations at A189 (blue; A189D or A189V) and S193 (purple; S193R or S193N) shown on A/California/04/2009 HA (PDB: 4jtv) for SFV018 2D01, SFV009 2G01, 240 IgA 1A03, 029–09 3A02, and 240 IgG 1A06, generated using A/Netherlands/602/2009 H1N1. The RBS is shown with a pink dashed circle. (E to G) CH65 binding to WT G189 (E), and steric clashes between L-CDR3 and HA resulting from G189D (F) and G189V (G) mutations in A/Solomon Islands/3/2006 HA (PDB:5ugy).
