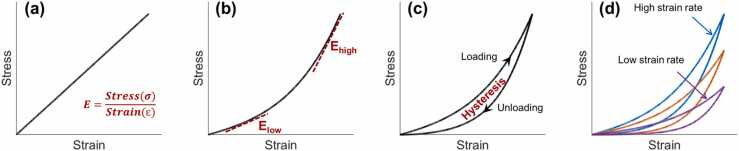
Fig. 2.
Demonstration of the stress–strain curves. (a) An ideal case of linear elastic material. (b) Nonlinear stress–strain relationship for a typical elastic material. (c) Hysteresis represents the difference between the strain energy required to generate given stress in the sample and the elastic energy at that stress. (d) The stress–strain curves and hysteresis loops are typically strain-rate-dependent in a viscoelastic material such as the cornea.