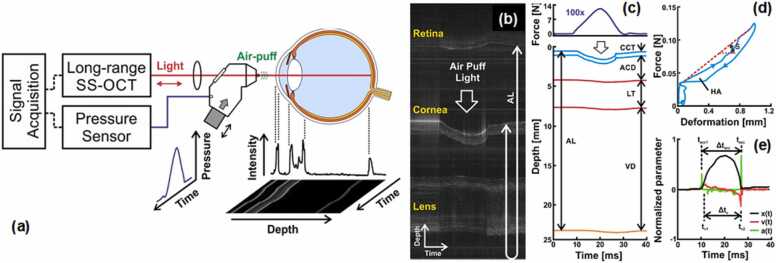
Fig. 10.
Estimation of corneal biomechanics by combining an SS-OCT with a commercial air-puff device from a non-contact tonometer. (a) Schematic of the air-puff OCE. (b–e) Representative air-pulse-induced dynamics of the ocular components (i.e., cornea, lens, and retina) from the right eye of a 23-year-old subject. (b) M-mode scan during the air-puff cycle. (c) Temporal force and displacement profiles. (d) Corneal hysteresis loop. (e) Air puff-induced corneal deformation, speed, and acceleration.
Reproduced from [164].