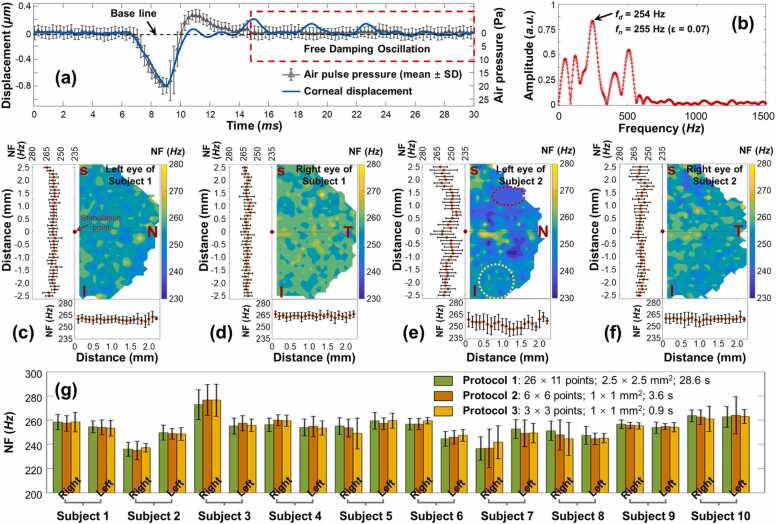
Fig. 12.
In vivo measurement of corneal natural frequency (NF) using a microliter air pulse OCE system (same as Fig. 11a) and the single degree of freedom (SDOF) modeling method (Section 5.2.2). (a) Typical profiles of air-pulse (20 Pa) and induced corneal displacement in a time series. The air pulse profile was calibrated as the means and standard deviations of 40 repeat measurements. The corneal damping oscillatory motion (in the red window) can be used for the SDOF analysis based on Eq. (7). (b) Fast Fourier transform for the corneal damping oscillations process. (c–f): Natural frequency (NF) characterization for ∼2.5 × 5 mm2 area (26 × 41 points; total time: 106.6 s) on the left and right corneas from two human subjects (air-pulse: 13 Pa). (g) Comparison of the NF (mean± SD) among three protocols with different measurement areas and time on 20 eyes from ten human subjects.
Reproduced from [49].