Figure 9. Effect of DAFP1 and TmAFP on the morphology and expression of functional markers in rat kidneys kept under hypothermic conditions.
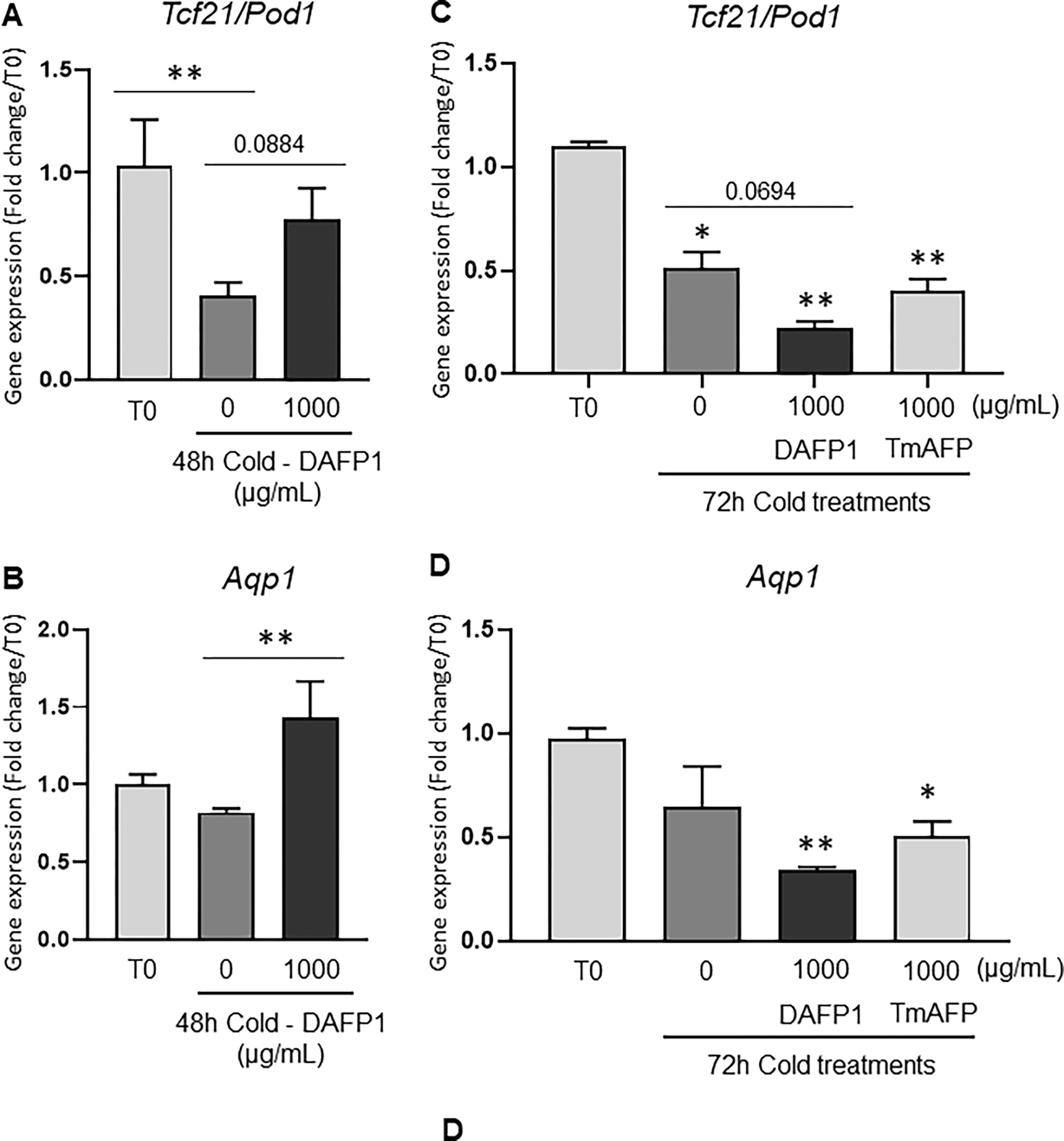
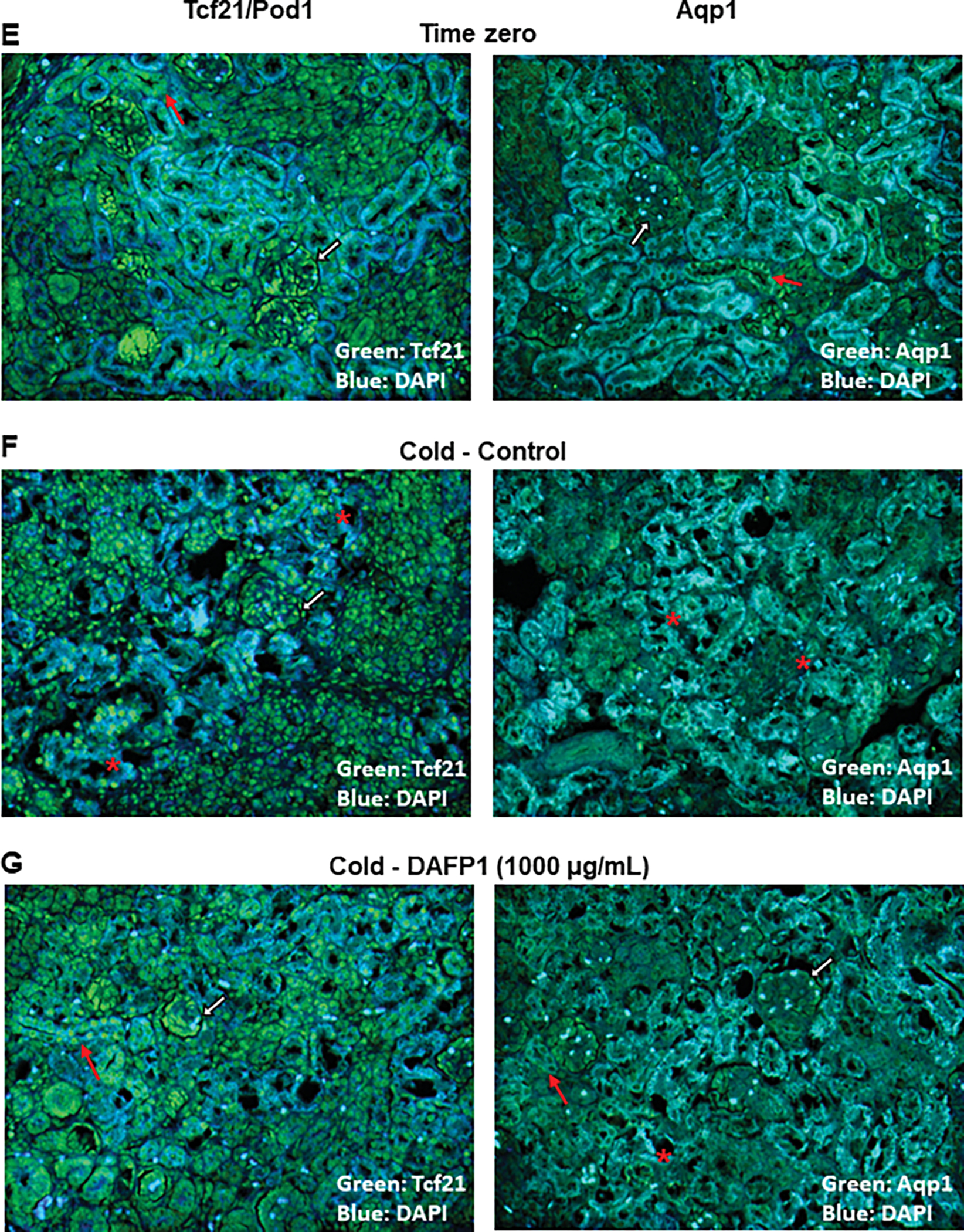
The expression of gene and protein levels of Aqp1 (Aquaporin water channel 1) and Tcf21 (Pod1) were examined in PND6 rat kidneys kept at 4°C for 48h (A, B, E-G) or 72h (C, D) in the presence of medium (Control/0) or 1000 μg/mL DAFP1 or TmAFP, in comparison to kidneys frozen at the time of dissection (Time zero; T0). The kidneys of 3 rats were used per condition for 48h cold exposure and 2 to 3 rats per condition for 72h cold exposure. After 48h cold treatment, for each rat, one kidney was frozen for mRNA analysis and the other kidney was fixed in paraformaldehyde for immunofluorescence analysis. After 72h cold treatment, all kidneys were processed for qPCR analysis. The mRNA levels of Tcf21 (A, C) and Aqp1 (B, D) were determined by qPCR analysis and normalized to GAPDH. Gene expression in control and DAFP1- or TmAFP- treated tissues kept in cold condition is expressed as fold change of the levels measured in samples frozen after dissection (T0). Statistical significance: * p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01. (E-G) Representative pictures showing the general morphology and immunofluorescence signals of Tcf21 and Aqp1 in kidneys at time zero (E) vs tissues kept at 4°C for 48h with medium (Control) (F) or 1000 μg/mL DAFP1 (G). White arrows point at glomeruli, red arrows point at tubules, and red stars indicate areas of tissue degeneration.
