FIGURE 2.
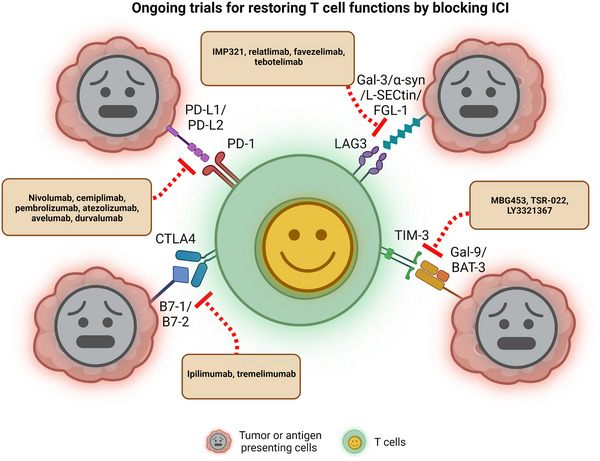
Blockade of ICI restores T cell function. Inhibition of PD‐1, CTLA4, TIM‐3, and LAG3 with interaction by antibodies, drugs, and peptides. The cytotoxic signal is released when the TCR recognizes an antigen on the membrane of tumor cells or (APCs). However, PD‐L1/2, B7‐1/2, Gal‐9/BAT‐3 and Gal‐3/α‐syn/L‐selectin/FGL‐1 are up‐regulated in tumor cells (APCs) when T cells are activated, resulting in inhibitory signals and dampening T cell activation by stimulatory signals. Clinical trials of blocking or inhibiting these interactions using antibodies or a newly designed combination, which restores T cell function and anti‐tumor immunity, are ongoing. Created with BioRender.com.Abbreviations: ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; PD‐1: Programmed cell death protein 1; CTLA4: Cytotoxic T‐lymphocyte associated protein 4; TIM‐3: T‐cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain 3; LAG3: Lymphocyte Activating 3; TCR: T cell receptor; APC: Antigen‐presenting cells; PD‐L1/2: ligands of PD‐1 (PD‐L1 and PD‐L2); Gal‐9: galectin‐9; BAT‐3: HLA‐B associated transcript 3; Gal‐3: Galectin‐3; α‐syn: Alpha‐synuclein; FGL‐1: Fibrinogen like 1.
