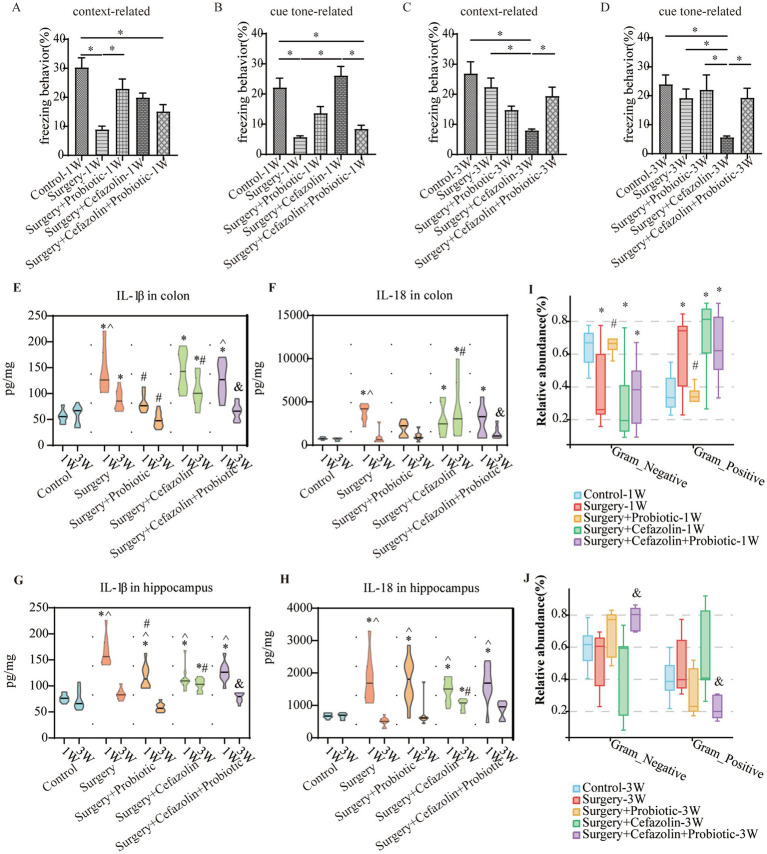
Figure 6.
The probiotics administration for surgery/anesthesia stress-induced and perioperative cefazolin-induced gut dysbacteria, and cognitive dysfunction, respectively. (A,B) Probiotics improved context-related (q = 5.58, p = 0.0024) but not cue tone-related (q = 3.597, p = 0.099) freezing behavior decreased by surgery/anesthesia stress at 1 week (n = 10, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (C,D) Surgery + cefazolin group showed a decreasing context-related (q = 6.984, p = 0.0001) and cue tone-related (q = 5.406, p = 0.0035) freezing behavior compared with the control group at 3 weeks; probiotics could improve these context-related (q = 4.224, p = 0.035) and cue tone-related (q = 4.024, p = 0.0495) freezing behavior (n = 10, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (E,F) ELISA: probiotics inhibited the increasing IL-1β (q = 5.183, p = 0.0078) in the colon at 1 week caused by surgery; probiotics inhibited the increasing IL-1β (q = 6.238, p = 0.0006) and IL-18 (q = 4.601, p = 0.0219) in the colon at 3 weeks after surgery compared with surgery + cefazolin group (n = 10, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (G,H) ELISA: probiotics inhibited the increasing IL-1β (q = 5.183, p = 0.0078) in the hippocampus at 1 week caused by surgery; probiotics inhibited the increasing IL-1β (q = 6.653, p = 0.0002) in the hippocampus at 3 weeks after surgery compared with surgery + cefazolin group (n = 10, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). (I,J) Probiotics could reverse the increasing relative abundance of gram-positive bacteria (q = 0.0083, p = 0.0028) and decreasing gram-negative bacteria (q = 0.0083, p = 0.0028) caused by surgery at 1 week, but not surgery + cefazolin; probiotics could reverse the increasing relative abundance of gram-positive bacteria (q = 0.0055, p = 0.0018) and decreasing gram-negative bacteria (q = 0.0055, p = 0.0018) caused by surgery + cefazolin at 3 weeks (n = 9, KW rank sum test with Wilcoxon rank sum test). Grp, group; CTL, control; S, surgery; SC, surgery combined with cefazolin; SP, surgery combined with probiotics; SCP, surgery combined with cefazolin and probiotics; G+, gram-positive bacteria; G−, gram-negative bacteria. *Compared with Grp CTL, p < 0.05; #compared with Grp S, p < 0.05; &compared with Grp SC, p < 0.05; ^compared with 3 weeks, p < 0.05.