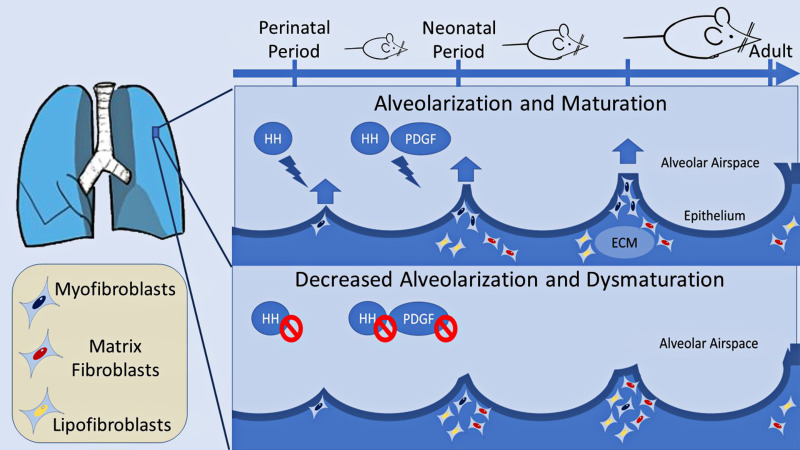
Figure 1.
Hedgehog (HH) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) control alveolar development and maturation by interacting with the mesenchyme. In HH and PDGF coreporter mice employed by Yie and colleagues (1), inhibition of either pathway leads to decreased alveolarization with abnormally enlarged alveoli and inhibition of secondary septation. The myofibroblast population is reduced after the pathway inhibition at a critical point of alveolar development in favor of lipofibroblasts and matrix fibroblasts. HH signaling is found to control downstream PDGF gene expression, indicative of cross-talk between the pathways. ECM = extracellular matrix.