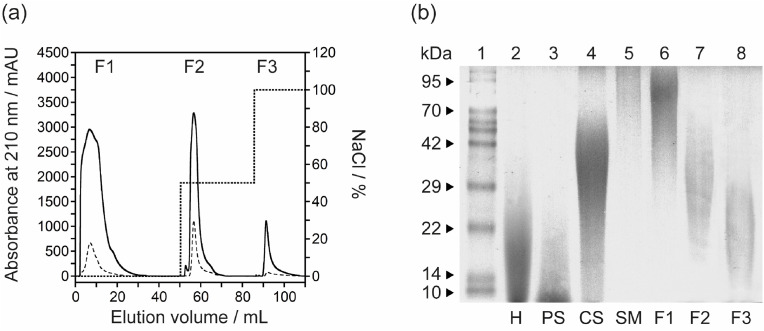
Fig. 1.
Establishment, purification and characterisation of the acharan sulfate from the mucus of A. fulica. (a) The purification of mGAG (solid line) from snail mucus by DEAE-Sepharose anion-exchange chromatography. The column was eluted with a stepwise salt gradient of 0.5 M–1.0 M NaCl (dotted line) in 50 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.5). The fractions were monitored at 210 nm and the flow rate was set at 2.5 mL/min. Three eluent fractions were collected; F1, non-interacting fraction; F2, eluted fraction at 0.5 M NaCl; and F3, eluted fraction at 1.0 M NaCl. The contamination of protein sample can be detected by measuring tis optical absorbance at 280 nm (dashed line). (b) PAGE analysis of mGAG-derived polysaccharides which visualized with alcian blue. Lane 1: Molecular weight protein markers, Lane 2: heparin (H), Lane 3: pentosan polysulfate (PS), Lane 4: chondroitin sulfate (CS), Lane 5: dried mGAG of snail mucus (SM), Lane 6: non-interacting fraction (F1), Lane 7: the papain-digested mGAG from DEAE-Sepharose at 0.5 M NaCl (F2), and Lane 8: the papain-digested mGAG from DEAE-Sepharose at 1.0 M NaCl (F3), respectively. The samples are loaded at the top of the gel (cathode) and migrate towards the anode at the bottom of the gel.