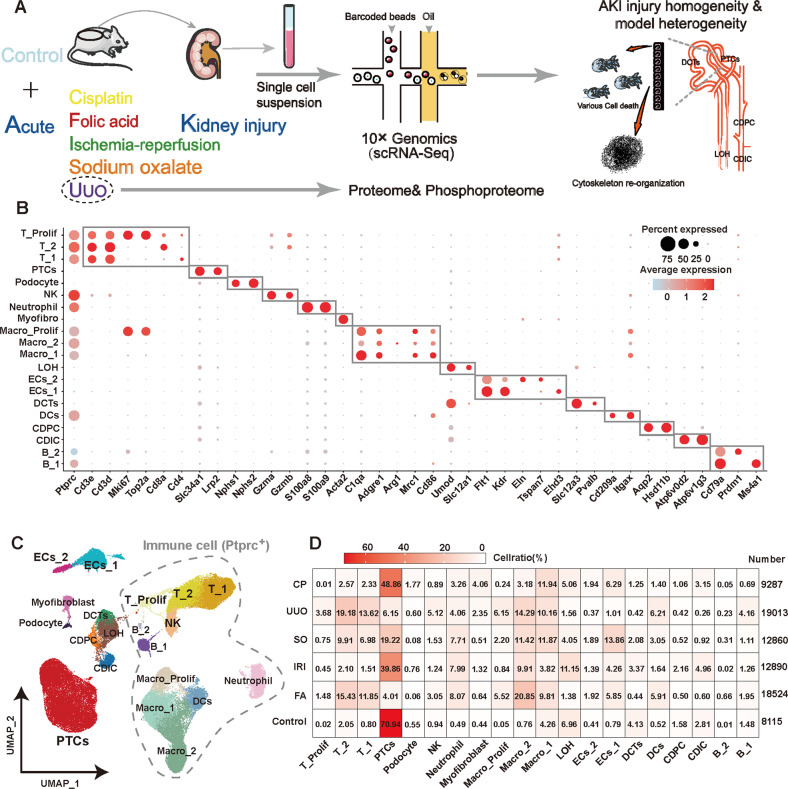
Fig. 1. The construction of the scRNA atlas initially explored the potential homogeneity and heterogeneity among different etiology-induced AKI.
A Study overview. Renal single-cell transcriptome sequencing was performed on control and five common mouse models of AKI: cisplatin kidney (CP), folic acid (FA), sodium oxalate (SO), ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI), and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Additionally, proteome and phosphorylated proteome was performed on UUO mouse kidneys to collectively reveal the potential homo- and heterogeneity of injury patterns in different etiology-induced AKI. B, C Data from 6 groups were integrated as a single dataset after data quality control and removal of batch effects. A total of 33 clusters were identified by unsupervised clustering, combined with top differentially expressed genes for each cluster and known cell markers for renal cell types, we identified a total of 20 cell subtypes, including 11 Ptptc (CD45) immune cells and 9 renal parenchymal cells. n = 2 each group. D Heatmap of model-celltype ratios. Compared with the IRI and CP models, the cell proportions of the FA, SO model are closer to those of the UUO model. n = 2 each group. Abbreviations: proximal tubular cells (PTCs), loop of Henle (LOH), distal convoluted tubules (DCTs), endothelial cells (ECs), collecting duct-principal cells (CDPC), collecting duct-intercalated cells (CDIC), dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer cells (NK), myofibroblasts (Myofibro), macrophage (Macro).