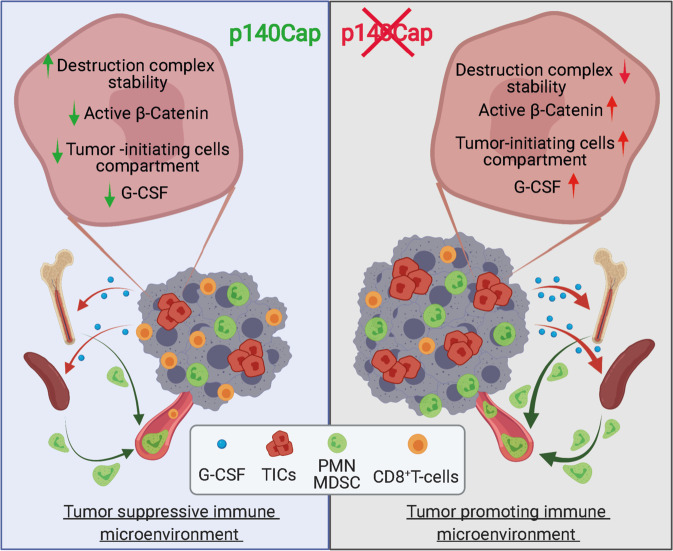
Fig. 10. p140Cap exerts a cell-extrinsic influence on the immune infiltrate composition of the tumor microenvironment, thereby favoring an effective anti-tumor immune response at the expense of a tumor-promoting inflammatory microenvironment.
Overall, this study shows that p140Cap activity is able to prevent tumor microenvironment infiltration through immunosuppressive PMN-MDSCs by inhibiting their systemic mobilization and local infiltration. Our functional studies in vitro and in vivo revealed that the decrease in G-CSF content is a function of the p140Cap ability to reduce the TIC compartment, which in turn is responsible for the production of G-CSF. The effect on the TIC compartment depends on the ability of p140Cap to enter and stabilize the β-Catenin destruction machinery, thereby inhibiting β-Catenin activity. Created with Biorender.com.