Fig. 1.
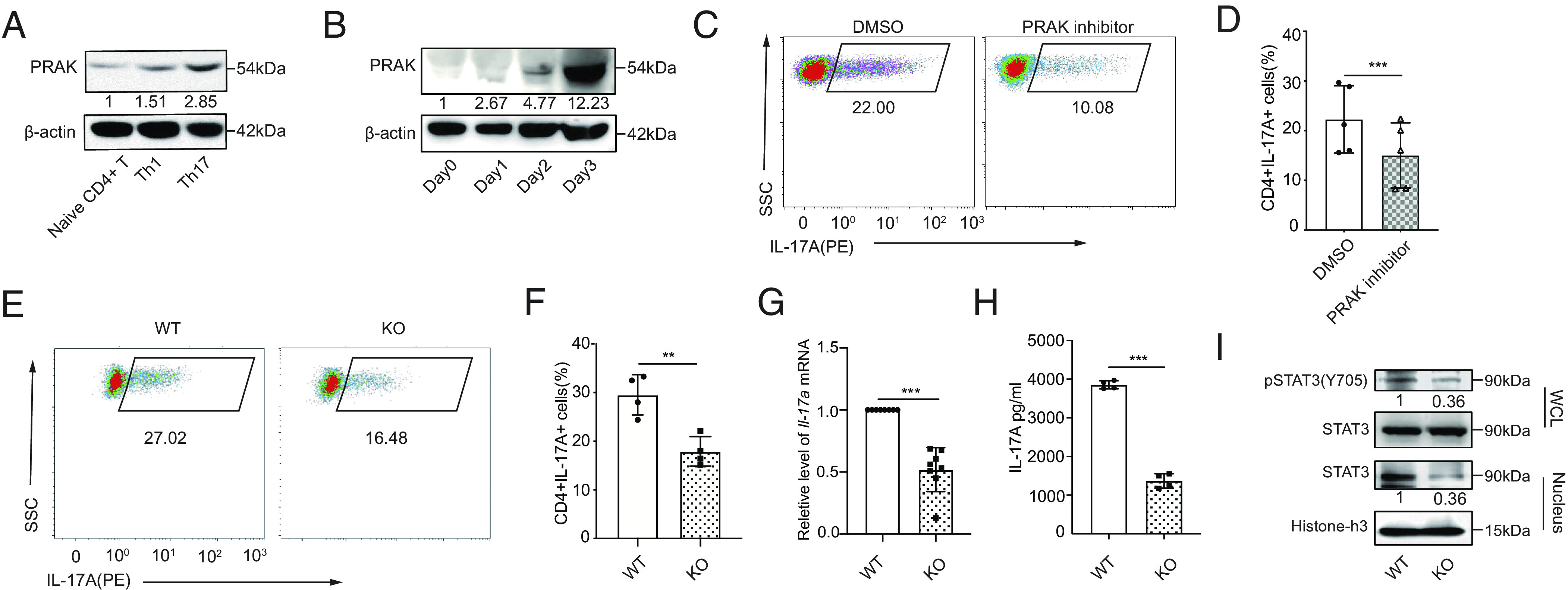
PRAK is essential for the differentiation of Th17 cells. Murine naïve CD4+ T cells were polarized into Th1(IFN-γ+IL-12) and Th17(TGF-β1+IL-6+anti-IL-4+anti-IFN-γ). (A) Immunoblot of PRAK protein in naïve CD4+ T cells and Th1, Th17 (n = 3). (B) PRAK expression in CD4+ T cells over the course of Th17 induction (n = 3). (C and D) Inhibition of Th17 cell differentiation by PRAK inhibitor GLPG0259. Representative dot plots are shown in C. Data from five independent experiments are presented as Mean ±SD (D). (E and F) Naïve CD4+ T cell from WT and Prak KO mice were cultured under Th17 polarization conditions for 3 days. IL-17A+ cells were detected by intracellular staining. Representative dot plots are shown in E. The percentage of IL-17A+ cells from four independent experiments are presented in F. Il-17a mRNA levels were assessed by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 8) (G). IL-17A in the supernatant was quantified by ELISA (n = 4) (H). Western botting was performed to detect total STAT3, nuclear STAT3 and Y705P STAT3 (n = 3). Representative blots were shown in (I). The numbers indicate the relative levels of pSTAT3 and nuclear STAT3 normalized against total STAT3 and histone-H3, respectively. The statistics was performed using Student’s t test. ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
