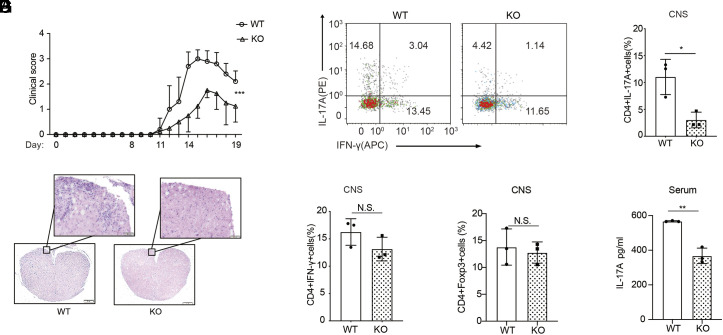
Fig. 2.
T cell-specific deletion of Prak alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). EAE model was established through MOG35-55 immunization. (A) Clinical scores were recorded from day 11. Data from 5 WT and 4 KO mice were analyzed by two-way ANOVA analysis. (B) Hematoxylin–eosin staining of spinal cord sections. (C–E) Intracellular staining of IL-17A and IFN-γ in the spinal cord infiltrating CD4+ T cells. Representative dot plots (C). Percentage of IL-17A+ (D) and IFN-γ+ (E) cells among CD4+ infiltrating T cells (n = 3). (F) Percentage of Foxp3+ cells in the spinal cord infiltrating CD4+ T cells (n = 3). (G) IL-17A levels in the serum of WT and KO mice, measured by ELISA (n = 3). The statistics was performed using Student’s t test. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; N.S not significant.