Fig. 4.
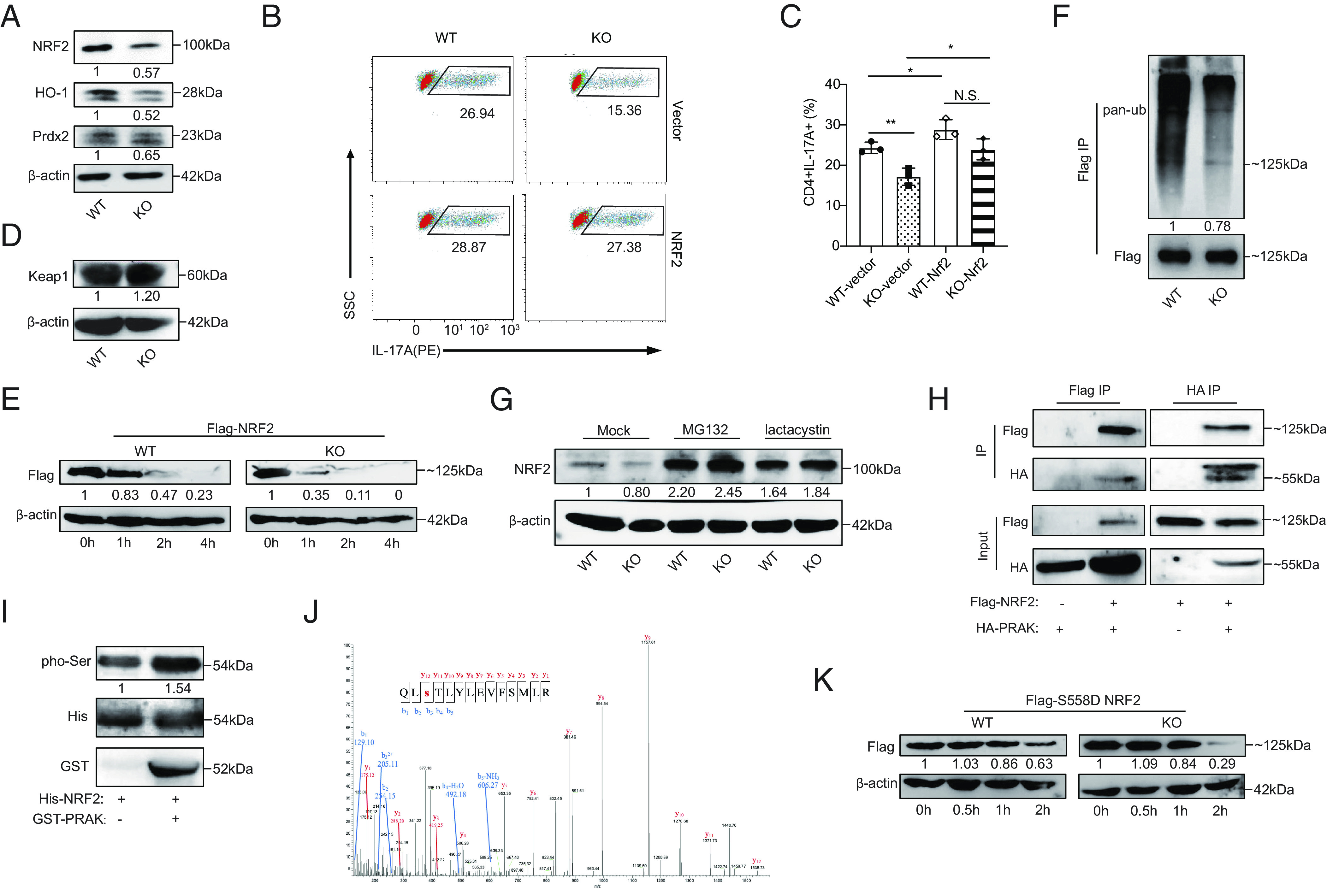
PRAK promotes redox homeostasis by stabilizing nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (NRF2). (A) Immunoblot of NRF2, HO-1, Prdx2 in WT and KO Th17 cells, densitometry performed using β-actin as loading control (n = 3). (B and C) WT and KO naïve CD4+ T cells were first transduced with Nrf2-expressing or empty vectors and then put into culture under Th17 polarizing conditions. IL-17A+ cells were detected by flow cytometry at day 3. Representative dot plots (B). Percentage of IL-17A+ cells (C) (n = 3). (D) Immunoblot of Keap1 in WT and KO Th17 cells (n = 3). (E) WT and PRAK KO HEK293T cells were transduced with equal amounts of Flag-tagged NRF2 plasmid. Cyclohexane (CHX) (200 μM) was added 24 h after transduction. Cells were harvested at various time points and examined for exogenous NRF2 expression by immunoblot. Densitometry was performed using β-actin as loading control (n = 3). (F) Ubiquitin modification of flag tagged NRF2 from WT and KO HEK293T, densitometry performed using Flag-NRF2 as control (n = 3). (G) Immunoblot of endogenous NRF2 in WT and KO Th17 cells after being polarized for 72 h with addition of 20 μM MG132, 5 μM lactacystin or isovolumetric DMSO in the last 12 h (n = 3). (H) Co-immunoprecipitation of HA-PRAK and Flag-NRF2 in HEK293T cells transduced with various combination of plasmids (n = 3). (I) In vitro kinase assay using purified His-NRF2 and GST-PRAK (n = 3). (J) Mass spectrum analysis of NRF2, purified from HEK293T, showing the phosphorylation on the Ser558 residual of NRF2. (K) Degradation of Flag-tagged S558D mutant of NRF2 in WT and PRAK KO HEK293T, assayed as in (D) (n = 3). The numbers indicate the relative protein levels normalized against β-actin and time 0.
